Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide: a bifunctional glucose-dependent regulator of glucagon and insulin secretion in humans
- PMID: 21984584
- PMCID: PMC3219957
- DOI: 10.2337/db11-0979
Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide: a bifunctional glucose-dependent regulator of glucagon and insulin secretion in humans
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the glucose dependency of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) effects on insulin and glucagon release in 10 healthy male subjects ([means ± SEM] aged 23 ± 1 years, BMI 23 ± 1 kg/m(2), and HbA(1c) 5.5 ± 0.1%).
Research design and methods: Saline or physiological doses of GIP were administered intravenously (randomized and double blinded) during 90 min of insulin-induced hypoglycemia, euglycemia, or hyperglycemia.
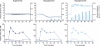
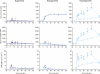
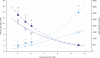
Results: During hypoglycemia, GIP infusion caused greater glucagon responses during the first 30 min compared with saline (76 ± 17 vs. 28 ± 16 pmol/L per 30 min, P < 0.008), with similar peak levels of glucagon reached after 60 min. During euglycemia, GIP infusion elicited larger glucagon responses (62 ± 18 vs. -11 ± 8 pmol/L per 90 min, P < 0.005). During hyperglycemia, comparable suppression of plasma glucagon (-461 ± 81 vs. -371 ± 50 pmol/L per 90 min, P = 0.26) was observed with GIP and saline infusions. In addition, during hyperglycemia, GIP more than doubled the insulin secretion rate (P < 0.0001).
Conclusions: In healthy subjects, GIP has no effect on glucagon responses during hyperglycemia while strongly potentiating insulin secretion. In contrast, GIP increases glucagon levels during fasting and hypoglycemic conditions, where it has little or no effect on insulin secretion. Thus, GIP seems to be a physiological bifunctional blood glucose stabilizer with diverging glucose-dependent effects on the two main pancreatic glucoregulatory hormones.
Figures

References
-
- Unger RH. Role of glucagon in the pathogenesis of diabetes: the status of the controversy. Metabolism 1978;27:1691–1709 - PubMed
-
- Gromada J, Franklin I, Wollheim CB. Alpha-cells of the endocrine pancreas: 35 years of research but the enigma remains. Endocr Rev 2007;28:84–116 - PubMed
-
- McIntosh CHS, Widenmaier S, Kim S-J. Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (gastric inhibitory polypeptide; GIP). Vitam Horm 2009;80:409–471 - PubMed
-
- Pederson RA, Brown JC. Interaction of gastric inhibitory polypeptide, glucose, and arginine on insulin and glucagon secretion from the perfused rat pancreas. Endocrinology 1978;103:610–615 - PubMed
-
- Elahi D, Andersen DK, Brown JC, et al. Pancreatic alpha- and beta-cell responses to GIP infusion in normal man. Am J Physiol 1979;237:E185–E191 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

