Autoreactive Tbet-positive CD4 T cells develop independent of classic Th1 cytokine signaling during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 21984703
- PMCID: PMC3709433
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100031
Autoreactive Tbet-positive CD4 T cells develop independent of classic Th1 cytokine signaling during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
Abstract
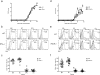
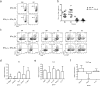
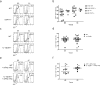
Many autoimmune chronic inflammatory diseases, including multiple sclerosis, are associated with the presence of Th1 and Th17 effector CD4 T cells. Paradoxically, the principal Th1 cytokine IFN-γ does not appear necessary for disease, but the key Th1-associated transcription factor Tbet has been reported to be essential for disease development. This conundrum propelled us to investigate the regulation of this transcription factor during autoimmunity. Following the onset of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, we observed a preferential upregulation of Tbet by CD4 T cells within the CNS, but not the secondary lymphoid organs. These Tbet-positive CD4 T cells were capable of producing the cytokine IFN-γ, and a proportion of these cells produced both IFN-γ and IL-17A. Interestingly, these Tbet-positive cells were present in high frequencies during disease in IFN-γ-deficient mice. Moreover, we found that CD4 T cells from IFN-γ-deficient/IFN-γ reporter mice upregulated the Thy1.1 reporter, indicating the presence of Th1 or Th1-like, Tbet-positive CD4 T cells even in the absence of the cardinal Th1 cytokine IFN-γ. These IFN-γ-deficient Th1-like cells not only maintain multiple Th1 properties but also exhibit increased expression of genes associated with the Th17 phenotype. We further examined the requirement of other Th1-associated molecules in controlling Tbet expression during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and noted that STAT1, IL-12, and IFN-γ were dispensable for the induction of Tbet in vivo. Hence, this study highlights the complex regulation of Tbet and the potential unrecognized role for Th1 cells during autoimmunity.
Figures


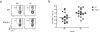
Similar articles
-
IL-7/IL-7 Receptor Signaling Differentially Affects Effector CD4+ T Cell Subsets Involved in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis.J Immunol. 2015 Sep 1;195(5):1974-83. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1403135. Epub 2015 Jul 29. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26223651 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 in helper T cells leads to defective Th17 differentiation by enhancing antagonistic effects of IFN-gamma on STAT3 and Smads.J Immunol. 2008 Mar 15;180(6):3746-56. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.6.3746. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18322180
-
T-bet is essential for Th1-mediated, but not Th17-mediated, CNS autoimmune disease.Eur J Immunol. 2013 Nov;43(11):2818-23. doi: 10.1002/eji.201343689. Epub 2013 Aug 21. Eur J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23878019 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Th17 cells in the pathogenesis of CNS inflammatory demyelination.J Neurol Sci. 2013 Oct 15;333(1-2):76-87. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2013.03.002. Epub 2013 Apr 8. J Neurol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23578791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Th1 versus Th17: are T cell cytokines relevant in multiple sclerosis?Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Feb;1812(2):246-51. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.05.012. Epub 2010 Jun 18. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 20600875 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
STAT4 controls GM-CSF production by both Th1 and Th17 cells during EAE.J Neuroinflammation. 2015 Jun 30;12:128. doi: 10.1186/s12974-015-0351-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2015. PMID: 26123499 Free PMC article.
-
Effector CD4 T cells with progenitor potential mediate chronic intestinal inflammation.J Exp Med. 2018 Jul 2;215(7):1803-1812. doi: 10.1084/jem.20172335. Epub 2018 Jun 18. J Exp Med. 2018. PMID: 29915024 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Oxidative Phosphorylation Regulates the Fate Decision between Pathogenic Th17 and Regulatory T Cells.Cell Rep. 2020 Feb 11;30(6):1898-1909.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.01.022. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 32049019 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptotic cell-treated dendritic cells induce immune tolerance by specifically inhibiting development of CD4⁺ effector memory T cells.Immunol Res. 2016 Feb;64(1):73-81. doi: 10.1007/s12026-015-8676-7. Immunol Res. 2016. PMID: 26111522 Free PMC article.
-
Autoimmunity in 2012.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2013 Oct;45(2):290-301. doi: 10.1007/s12016-013-8386-7. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23975606 Review.
References
-
- Sospedra M, Martin R. Immunology of multiple sclerosis. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:683–747. - PubMed
-
- Harrington L, Hatton R, Mangan P, Turner H, Murphy T, Murphy K, Weaver C. Interleukin 17-producing CD4+ effector T cells develop via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:1123–1132. - PubMed
-
- Szabo S, Kim S, Costa G, Zhang X, Fathman C, Glimcher L. A novel transcription factor, T-bet, directs Th1 lineage commitment. Cell. 2000;100:655–669. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

