MiMIC: a highly versatile transposon insertion resource for engineering Drosophila melanogaster genes
- PMID: 21985007
- PMCID: PMC3191940
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.1662
MiMIC: a highly versatile transposon insertion resource for engineering Drosophila melanogaster genes
Abstract
We demonstrate the versatility of a collection of insertions of the transposon Minos-mediated integration cassette (MiMIC), in Drosophila melanogaster. MiMIC contains a gene-trap cassette and the yellow+ marker flanked by two inverted bacteriophage ΦC31 integrase attP sites. MiMIC integrates almost at random in the genome to create sites for DNAmanipulation. The attP sites allow the replacement of the intervening sequence of the transposon with any other sequence through recombinase-mediated cassette exchange (RMCE). We can revert insertions that function as gene traps and cause mutant phenotypes to revert to wild type by RMCE and modify insertions to control GAL4 or QF overexpression systems or perform lineage analysis using the Flp recombinase system. Insertions in coding introns can be exchanged with protein-tag cassettes to create fusion proteins to follow protein expression and perform biochemical experiments. The applications of MiMIC vastly extend the D. melanogaster toolkit.
Figures
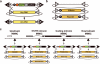
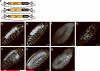
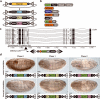
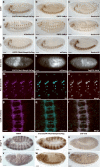
Comment in
-
'MiMICing' genomic flexibility.Nat Methods. 2011 Aug 30;8(9):728-9. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1672. Nat Methods. 2011. PMID: 21878919
References
-
- Ryder E, Russell S. Transposable elements as tools for genomics and genetics in Drosophila. Brief. Funct. Genomic. Proteomic. 2003;2:57–71. - PubMed
-
- Venken KJ, Bellen HJ. Emerging technologies for gene manipulation in Drosophila melanogaster. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005;6:167–178. - PubMed
-
- Venken KJ, Bellen HJ. Transgenesis upgrades for Drosophila melanogaster. Development. 2007;134:3571–3584. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

