Clozapine, but not olanzapine, disrupts conditioned avoidance response in rats by antagonizing 5-HT2A/2C receptors
- PMID: 21986871
- PMCID: PMC3275656
- DOI: 10.1007/s00702-011-0722-6
Clozapine, but not olanzapine, disrupts conditioned avoidance response in rats by antagonizing 5-HT2A/2C receptors
Abstract
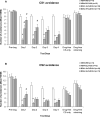
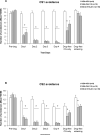
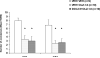
The present study was designed to assess the role of 5-HT(2A/2C) receptors in the acute and repeated effect of clozapine and olanzapine in a rat conditioned avoidance response model, a validated model of antipsychotic activity. Male Sprague-Dawley rats that were previously treated with either phencyclidine (0.5-2.0 mg/kg, sc), amphetamine (1.25-5.0 mg/kg, sc), or saline and tested in a prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle study were used. They were first trained to acquire avoidance response to a white noise (CS1) and a pure tone (CS2) that differed in their ability to predict the occurrence of footshock. Those who acquired avoidance response were administered with clozapine (10.0 mg/kg, sc) or olanzapine (1.0 mg/kg, sc) together with either saline or 1-2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo-amphetamine (DOI, a selective 5-HT(2A/2C) agonist, 1.0 or 2.5 mg/kg, sc), and their conditioned avoidance responses were tested for four consecutive days. After two drug-free retraining days, the long-term repeated effect was assessed in a challenge test during which all rats were injected with a low dose of clozapine (5 mg/kg, sc) or olanzapine (0.5 mg/kg). Results show that pretreatment of DOI dose-dependently reversed the acute disruptive effect of clozapine on both CS1 and CS2 avoidance responses, whereas it had little effect in reversing the acute effect of olanzapine. On the challenge test, pretreatment of DOI did not alter the clozapine-induced tolerance or the olanzapine-induced sensitization effect. These results confirmed our previous findings and suggest that clozapine, but not olanzapine, acts on through 5-HT(2A/2C) receptors to achieve its acute avoidance disruptive effect and likely its therapeutic effects. The long-term clozapine tolerance and olanzapine sensitization effects appear to be mediated by non-5-HT(2A/2C) receptors.
Figures
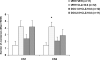
References
-
- Ader R, Clink DW. Effects of chlorpromazine on the acquisition and extinction of an avoidance response in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1957;131:144–148. - PubMed
-
- Arnt J. Pharmacological specificity of conditioned avoidance response inhibition in rats: inhibition by neuroleptics and correlation to dopamine receptor blockade. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1982;51:321–329. - PubMed
-
- Atkins JB, Chlan-Fourney J, Nye HE, Hiroi N, Carlezon WA, Jr, Nestler EJ. Region-specific induction of deltaFosB by repeated administration of typical versus atypical antipsychotic drugs. Synapse. 1999;33:118–128. - PubMed
-
- Barrett JE. The emergence of behavioral pharmacology. Mol Interv. 2002;2:470–475. - PubMed
-
- Barrett JE, Bergman J. Peter B. Dews and pharmacological studies on behavior. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008;326:683–690. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

