Two distinct subtypes of hepatitis B virus-related acute liver failure are separable by quantitative serum immunoglobulin M anti-hepatitis B core antibody and hepatitis B virus DNA levels
- PMID: 21987355
- PMCID: PMC3272543
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.24732
Two distinct subtypes of hepatitis B virus-related acute liver failure are separable by quantitative serum immunoglobulin M anti-hepatitis B core antibody and hepatitis B virus DNA levels
Abstract
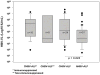
Hepatitis B virus (HBV)-related acute liver failure (HBV-ALF) may occur after acute HBV infection (AHBV-ALF) or during an exacerbation of chronic HBV infection (CHBV-ALF). Clinical differentiation of the two is often difficult if a previous history of HBV is not available. Quantitative measurements of immunoglobulin M (IgM) anti-hepatitis B core antibody (anti-HBc) titers and of HBV viral loads (VLs) might allow the separation of AHBV-ALF from CHBV-ALF. Of 1,602 patients with ALF, 60 met clinical criteria for AHBV-ALF and 27 for CHBV-ALF. Sera were available on 47 and 23 patients, respectively. A quantitative immunoassay was used to determine IgM anti-HBc levels, and real-time polymerase chain reaction (rtPCR) was used to determine HBV VLs. AHBV-ALFs had much higher IgM anti-HBc titers than CHBV-ALFs (signal-to-noise [S/N] ratio median: 88.5; range, 0-1,120 versus 1.3, 0-750; P < 0.001); a cut point for a S/N ratio of 5.0 correctly identified 44 of 46 (96%) AHBV-ALFs and 16 of 23 (70%) CHBV-ALFs; the area under the receiver operator characteristic curve was 0.86 (P < 0.001). AHBV-ALF median admission VL was 3.9 (0-8.1) log10 IU/mL versus 5.2 (2.0-8.7) log10 IU/mL for CHBV-ALF (P < 0.025). Twenty percent (12 of 60) of the AHBV-ALF group had no hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) detectable on admission to study, wheras no CHBV-ALF patients experienced HBsAg clearance. Rates of transplant-free survival were 33% (20 of 60) for AHBV-ALF versus 11% (3 of 27) for CHBV-ALF (P = 0.030).
Conclusions: AHBV-ALF and CHBV-ALF differ markedly in IgM anti-HBc titers, in HBV VLs, and in prognosis, suggesting that the two forms are, indeed, different entities that might each have a unique pathogenesis.
Copyright © 2011 American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures



References
-
- Inoue K, Yoshiba M, Sekiyama K, Okamoto H, Mayumi M. Clinical and molecular virological differences between fulminant hepatic failures following acute and chronic infection with hepatitis B virus. J Med Virol. 1998;55:35–41. - PubMed
-
- Umemura T, Tanaka E, Kiyosawa K, Kumada H. Mortality secondary to fulminant hepatic failure in patients with prior resolution of hepatitis B virus infection in Japan. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47:e52–56. - PubMed
-
- Hoofnagle JH, Doo E, Liang TJ, Fleischer R, Lok AS. Management of hepatitis B: summary of a clinical research workshop. Hepatology. 2007;45:1056–1075. - PubMed
-
- Lee WM. Hepatitis B virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:1733–1745. - PubMed
-
- Krogsgaard K, Kryger P, Aldershvile J, Andersson P, Brechot C. Hepatitis B virus DNA in serum from patients with acute hepatitis B. Hepatology. 1985;5:10–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
