Disruption of nitric oxide signaling by Helicobacter pylori results in enhanced inflammation by inhibition of heme oxygenase-1
- PMID: 21987660
- PMCID: PMC3208050
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102111
Disruption of nitric oxide signaling by Helicobacter pylori results in enhanced inflammation by inhibition of heme oxygenase-1
Abstract
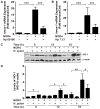
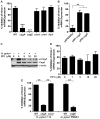
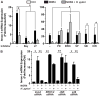
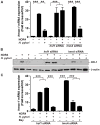
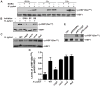
A strong cellular cross-talk exists between the pathogen Helicobacter pylori and high-output NO production. However, how NO and H. pylori interact to signal in gastric epithelial cells and modulate the innate immune response is unknown. We show that chemical or cellular sources of NO induce the anti-inflammatory effector heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) in gastric epithelial cells through a pathway that requires NF-κB. However, H. pylori decreases NO-induced NF-κB activation, thereby inhibiting HO-1 expression. This inhibitory effect of H. pylori results from activation of the transcription factor heat shock factor-1 by the H. pylori virulence factor CagA and by the host signaling molecules ERK1/2 and JNK. Consistent with these findings, HO-1 is downregulated in gastric epithelial cells of patients infected with cagA(+) H. pylori but not in gastric epithelial cells of patients infected with cagA(-) H. pylori. Enhancement of HO-1 activity in infected cells or in H. pylori-infected mice inhibits chemokine generation and reduces inflammation. These data define a mechanism by which H. pylori favors its own pathogenesis by inhibiting HO-1 induction through the action of CagA.
Figures






References
-
- Blaser MJ, Perez-Perez GI, Kleanthous H, Cover TL, Peek RM, Chyou PH, Stemmermann GN, Nomura A. Infection with Helicobacter pylori strains possessing cagA is associated with an increased risk of developing adenocarcinoma of the stomach. Cancer Res. 1995;55:2111–2115. - PubMed
-
- Odenbreit S, Puls J, Sedlmaier B, Gerland E, Fischer W, Haas R. Translocation of Helicobacter pylori CagA into gastric epithelial cells by type IV secretion. Science. 2000;287:1497–1500. - PubMed
-
- Selbach M, Moese S, Hauck CR, Meyer TF, Backert S. Src is the kinase of the Helicobacter pylori CagA protein in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:6775–6778. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01CA116087/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK058404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 RR024977/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA116087/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009592/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30DK058404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK058587/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK053620/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01CA028842/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK053620/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA028842/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA077955/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01AT004821/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AT004821/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- TL1 RR024978/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

