Autoantibodies recognizing carbamylated proteins are present in sera of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and predict joint damage
- PMID: 21987802
- PMCID: PMC3198314
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1114465108
Autoantibodies recognizing carbamylated proteins are present in sera of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and predict joint damage
Abstract
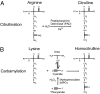
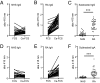
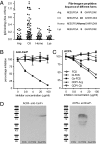
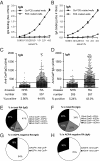
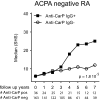
Autoimmune responses against posttranslationally modified antigens are a hallmark of several autoimmune diseases. For example, antibodies against citrullinated protein antigens (ACPA) have shown their relevance for the prognosis and diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and have been implicated in disease pathogenesis. It is conceivable that other autoantibody systems, recognizing other posttranslationally modified proteins, are also present in RA. Here, we describe the presence of an autoantibody system that discriminates between citrulline- and homocitrulline-containing antigens in the sera of RA-patients. IgG antibodies recognizing carbamylated (homocitrulline-containing) antigens were present in sera of over 45% of RA-patients. Likewise, anticarbamylated protein (anti-CarP) IgA antibodies were observed in 43% of RA-sera. ACPA and anti-CarP antibodies are distinct autoantibodies because, in selected double-positive patients, the anti-CarP antibody binding to carbamylated antigens could be inhibited by carbamylated antigens, but not by control or citrullinated antigens. Similarly, ACPA-binding to citrullinated antigens could only be inhibited by citrullinated antigens. In line with this observation, 16% of ACPA-negative RA-patients, as measured by a standard ACPA assay, harbored IgG anti-CarP antibodies, whereas 30% of these patients tested positive for IgA anti-CarP antibodies. The presence of anti-CarP antibodies was predictive for a more severe disease course in ACPA-negative patients as measured by radiological progression. Taken together, these data show the presence of a unique autoantibody system recognizing carbamylated, but not citrullinated, protein antigens. These antibodies are predictive for a more severe clinical course in ACPA-negative RA-patients, indicating that anti-CarP antibodies are a unique and relevant serological marker for ACPA-negative RA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
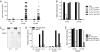
References
-
- Klareskog L, Rönnelid J, Lundberg K, Padyukov L, Alfredsson L. Immunity to citrullinated proteins in rheumatoid arthritis. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008;26:651–675. - PubMed
-
- van der Woude D, et al. Prevalence of and predictive factors for sustained disease-modifying antirheumatic drug-free remission in rheumatoid arthritis: Results from two large early arthritis cohorts. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60:2262–2271. - PubMed
-
- Visser K, et al. Pretreatment serum levels of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies are associated with the response to methotrexate in recent-onset arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67:1194–1195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

