Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega
- PMID: 21988835
- PMCID: PMC3261699
- DOI: 10.1038/msb.2011.75
Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega
Abstract
Multiple sequence alignments are fundamental to many sequence analysis methods. Most alignments are computed using the progressive alignment heuristic. These methods are starting to become a bottleneck in some analysis pipelines when faced with data sets of the size of many thousands of sequences. Some methods allow computation of larger data sets while sacrificing quality, and others produce high-quality alignments, but scale badly with the number of sequences. In this paper, we describe a new program called Clustal Omega, which can align virtually any number of protein sequences quickly and that delivers accurate alignments. The accuracy of the package on smaller test cases is similar to that of the high-quality aligners. On larger data sets, Clustal Omega outperforms other packages in terms of execution time and quality. Clustal Omega also has powerful features for adding sequences to and exploiting information in existing alignments, making use of the vast amount of precomputed information in public databases like Pfam.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
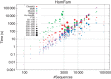
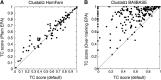
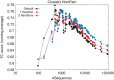
References
-
- Arthur D, Vassilvitskii S (2007) k-means++: the advantages of careful seeding. Proceedings of the Eighteenth Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms. pp 1027–1035
-
- Clamp M, Cuff J, Searle SM, Barton GJ (2004) The Jalview Java alignment editor. Bioinformatics 20: 426–427 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

