A prior feature SVM-MRF based method for mouse brain segmentation
- PMID: 21988893
- PMCID: PMC3508710
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.09.053
A prior feature SVM-MRF based method for mouse brain segmentation
Abstract
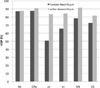
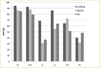
We introduce an automated method, called prior feature Support Vector Machine-Markov Random Field (pSVMRF), to segment three-dimensional mouse brain Magnetic Resonance Microscopy (MRM) images. Our earlier work, extended MRF (eMRF) integrated Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Markov Random Field (MRF) approaches, leading to improved segmentation accuracy; however, the computation of eMRF is very expensive, which may limit its performance on segmentation and robustness. In this study pSVMRF reduces training and testing time for SVM, while boosting segmentation performance. Unlike the eMRF approach, where MR intensity information and location priors are linearly combined, pSVMRF combines this information in a nonlinear fashion, and enhances the discriminative ability of the algorithm. We validate the proposed method using MR imaging of unstained and actively stained mouse brain specimens, and compare segmentation accuracy with two existing methods: eMRF and MRF. C57BL/6 mice are used for training and testing, using cross validation. For formalin fixed C57BL/6 specimens, pSVMRF outperforms both eMRF and MRF. The segmentation accuracy for C57BL/6 brains, stained or not, was similar for larger structures like hippocampus and caudate putamen, (~87%), but increased substantially for smaller regions like susbtantia nigra (from 78.36% to 91.55%), and anterior commissure (from ~50% to ~80%). To test segmentation robustness against increased anatomical variability we add two strains, BXD29 and a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Segmentation accuracy for new strains is 80% for hippocampus, and caudate putamen, indicating that pSVMRF is a promising approach for phenotyping mouse models of human brain disorders.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Automated segmentation of mouse brain images using extended MRF.Neuroimage. 2009 Jul 1;46(3):717-25. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.02.012. Epub 2009 Feb 21. Neuroimage. 2009. PMID: 19236923 Free PMC article.
-
Automated segmentation of neuroanatomical structures in multispectral MR microscopy of the mouse brain.Neuroimage. 2005 Aug 15;27(2):425-35. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.04.017. Neuroimage. 2005. PMID: 15908233
-
A segmentation of brain MRI images utilizing intensity and contextual information by Markov random field.Comput Assist Surg (Abingdon). 2017 Dec;22(sup1):200-211. doi: 10.1080/24699322.2017.1389398. Epub 2017 Oct 26. Comput Assist Surg (Abingdon). 2017. PMID: 29072503
-
Artificial intelligence for brain neuroanatomical segmentation in magnetic resonance imaging: A literature review.J Clin Neurosci. 2025 Apr;134:111073. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2025.111073. Epub 2025 Jan 28. J Clin Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39879724 Review.
-
Fully automated whole-head segmentation with improved smoothness and continuity, with theory reviewed.PLoS One. 2015 May 18;10(5):e0125477. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125477. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25992793 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Magnetic resonance image tissue classification using an automatic method.Diagn Pathol. 2014 Dec 24;9:207. doi: 10.1186/s13000-014-0207-7. Diagn Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25540017 Free PMC article.
-
Microcephaly with altered cortical layering in GIT1 deficiency revealed by quantitative neuroimaging.Magn Reson Imaging. 2021 Feb;76:26-38. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2020.09.023. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Magn Reson Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33010377 Free PMC article.
-
An End-to-end System for Automatic Characterization of Iba1 Immunopositive Microglia in Whole Slide Imaging.Neuroinformatics. 2019 Jul;17(3):373-389. doi: 10.1007/s12021-018-9405-x. Neuroinformatics. 2019. PMID: 30406865
-
Quantitative mapping of trimethyltin injury in the rat brain using magnetic resonance histology.Neurotoxicology. 2014 May;42:12-23. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2014.02.009. Epub 2014 Mar 11. Neurotoxicology. 2014. PMID: 24631313 Free PMC article.
-
Connectivity characterization of the mouse basolateral amygdalar complex.Nat Commun. 2021 May 17;12(1):2859. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22915-5. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34001873 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe S. Support Vector Machines for Pattern Classification (Advances in Pattern Recognition) Secaucus, NJ: Springer-Verlag New York, Inc.; 2005.
-
- Ali AA, Dale AM, Badea A, Johnson GA. Automated segmentation of neuroanatomical structures in multispectral MR microscopy of the mouse brain. NeuroImage. 2005;27(2):425–435. - PubMed
-
- Awate SP, Tasdizen T, Foster N, Whitaker RT. Adaptive Markov modeling for mutualinformation- based, unsupervised MRI brain-tissue classification. Medical Image Analysis. 2006;10:726–739. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

