Electrosensory ampullary organs are derived from lateral line placodes in bony fishes
- PMID: 21988912
- PMCID: PMC4212271
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms1502
Electrosensory ampullary organs are derived from lateral line placodes in bony fishes
Abstract
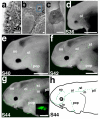
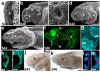
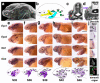
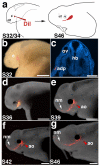
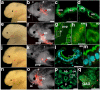
Electroreception is an ancient subdivision of the lateral line sensory system, found in all major vertebrate groups (though lost in frogs, amniotes and most ray-finned fishes). Electroreception is mediated by 'hair cells' in ampullary organs, distributed in fields flanking lines of mechanosensory hair cell-containing neuromasts that detect local water movement. Neuromasts, and afferent neurons for both neuromasts and ampullary organs, develop from lateral line placodes. Although ampullary organs in the axolotl (a representative of the lobe-finned clade of bony fishes) are lateral line placode-derived, non-placodal origins have been proposed for electroreceptors in other taxa. Here we show morphological and molecular data describing lateral line system development in the basal ray-finned fish Polyodon spathula, and present fate-mapping data that conclusively demonstrate a lateral line placode origin for ampullary organs and neuromasts. Together with the axolotl data, this confirms that ampullary organs are ancestrally lateral line placode-derived in bony fishes.
Figures
References
-
- Coombs S, Montgomery JC. The enigmatic lateral line system. In: Popper AN, Fay RR, editors. Comparative Hearing: Fishes and Amphibians. Springer-Verlag; New York: 1999. pp. 319–362.
-
- Bullock TH, Hopkins CD, Popper AN, Fay RR. Electroreception. Springer; New York: 2005.
-
- Bodznick D, Montgomery JC. The physiology of low-frequency electrosensory systems. In: Bullock TH, Hopkins CD, Popper AN, Fay RR, editors. Electroreception. Springer; New York: 2005. pp. 132–153.
-
- Jørgensen JM. Morphology of electroreceptive sensory organs. In: Bullock TH, Hopkins CD, Popper AN, Fay RR, editors. Electroreception. Springer; New York: 2005. pp. 47–67.
-
- Northcutt RG. Evolution of gnathostome lateral line ontogenies. Brain Behav. Evol. 1997;50:25–37. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

