Diarrhea is a major killer of children with severe acute malnutrition admitted to inpatient set-up in Lusaka, Zambia
- PMID: 21989455
- PMCID: PMC3214843
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2891-10-110
Diarrhea is a major killer of children with severe acute malnutrition admitted to inpatient set-up in Lusaka, Zambia
Abstract
Introduction: Mortality of children with Severe Acute Malnutrition (SAM) in inpatient set-ups in sub-Saharan Africa still remains unacceptably high. We investigated the prevalence and effect of diarrhea and HIV infection on inpatient treatment outcome of children with complicated SAM receiving treatment in inpatient units.
Method: A cohort of 430 children aged 6-59 months old with complicated SAM admitted to Zambia University Teaching Hospital's stabilization centre from August to December 2009 were followed. Data on nutritional status, socio-demographic factors, and admission medical conditions were collected up on enrollment. T-test and chi-square tests were used to compare difference in mean or percentage values. Logistic regression was used to assess risk of mortality by admission characteristics.
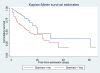
Results: Majority, 55.3% (238/430) were boys. The median age of the cohort was 17 months (inter-quartile range, IQR 12-22). Among the children, 68.9% (295/428) had edema at admission. The majority of the children, 67.3% (261/388), presented with diarrhea; 38.9% (162/420) tested HIV positive; and 40.5% (174/430) of the children died. The median Length of stay of the cohort was 9 days (IQR, 5-14 days); 30.6% (53/173) of the death occurred within 48 hours of admission. Children with diarrhea on admission had two and half times higher odds of mortality than those without diarrhea; Adjusted OR = 2.5 (95% CI 1.50-4.09, P < 0.001). The odds of mortality for children with HIV infection was higher than children without HIV infection; Adjusted OR = 1.6 (95% CI 0.99-2.48 P = 0.5).
Conclusion: Diarrhea is a major cause of complication in children with severe acute malnutrition. Under the current standard management approach, diarrhea in children with SAM was found to increase their odds of death substantially irrespective of other factors.
Figures
References
-
- Black RE, Cousens S, Johnson HL, Lawn JE, Rudan I, Bassani DG, Jha P, Campbell H, Walker CF, Cibulskis R, Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality in 2008: a systematic analysis. Lancet. pp. 1969–1987. - PubMed
-
- Pelletier DL. The relationship between child anthropometry and mortality in developing countries: implications for policy, programs and future research. J Nutr. 1994;124(10 Suppl):2047S–2081S. - PubMed
-
- Community-based management of Severe Acute Malnutrition-A Joint Statement by the World Health Organization, the World Food Programme, the United Nations Standing Committee on Nutrition and the United Nations Children's Fund. 2007. Geneva, UN press.2007
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical