Solitaire FR thrombectomy system: immediate results in 56 consecutive acute ischemic stroke patients
- PMID: 21990438
- PMCID: PMC3240775
- DOI: 10.1136/jnis.2010.004051
Solitaire FR thrombectomy system: immediate results in 56 consecutive acute ischemic stroke patients
Abstract
Background and purpose: Prompt recanalization of cerebral arteries in patients diagnosed with acute ischemic stroke is known to be associated with a better clinical outcome. The aim of this study was to present our initial experience regarding the efficacy and safety of the Solitaire FR as a revascularization device.
Methods: 56 consecutive patients presenting with acute ischemic stroke underwent intra-arterial therapy using the Solitaire FR revascularization device. Immediate angiographic results and early clinical outcomes are presented.
Results: Solitaire FR was successful in achieving recanalization in 50 out of 56 patients (89%) with a final Thrombolysis in Cerebral Infarction score ≥2b. Five out of 56 patients had procedure related complications: two asymptomatic subarachnoid hemorrhages, two thromboembolic events and one symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (PH2). Thirty patients (53.5%) demonstrated at discharge a National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale Score of ≤1 or an improvement of at least 10 points from baseline, and 26 patients (46%) had a modified Rankin Score ≤2.
Conclusions: Solitaire FR is successful in achieving a high rate of arterial recanalization with a low complication rate. The Solitaire FR is a promising thrombectomy tool with a high degree of effectiveness, safety and ease of use.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
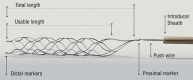
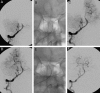

Comment in
-
Stroke etiology determines effectiveness of retrievable stents.J Neurointerv Surg. 2014 Mar;6(2):e11. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2012-010395. Epub 2012 May 16. J Neurointerv Surg. 2014. PMID: 22591732 No abstract available.
References
-
- Rha JH, Saver JL. The impact of recanalization on ischemic stroke outcome: a meta-analysis. Stroke 2007;38:967–73. - PubMed
-
- . Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke: The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. N Engl J Med 1995;333:1581–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
