Recombinase-mediated cassette exchange as a novel method to study somatic hypermutation in Ramos cells
- PMID: 21990614
- PMCID: PMC3190358
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.00186-11
Recombinase-mediated cassette exchange as a novel method to study somatic hypermutation in Ramos cells
Abstract
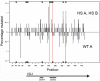
Activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) mediates the somatic hypermutation (SHM) of immunoglobulin (Ig) variable (V) regions that is required for the generation of antibody diversity and for the affinity maturation of the antibody response against infectious agents and toxic substances. AID preferentially targets WRC (W = A/T, R = A/G) hot spot motifs, particularly WGCW motifs that create overlapping hot spots on both strands. In order to gain a better understanding of the generation of antibody diversity and to create a platform for the in vitro generation of affinity-matured antibodies, we have established a system involving recombinase-mediated cassette exchange (RMCE) to replace the V region and its flanking sequences. This makes it possible to easily manipulate the sequence of the Ig gene within the endogenous heavy chain of the Ramos human Burkitt's lymphoma cell line. Here we show that the newly integrated wild-type (WT) VH regions introduced by RMCE undergo SHM similarly to non-RMCE-modified Ramos cells. Most importantly, we have shown that introducing a cluster of WGCW motifs into the complementary determining region 2 (CDR2) of the human heavy chain V region significantly raised the mutation frequency and number of mutations per sequence compared to WT controls. Thus, we have demonstrated a novel platform in Ramos cells whereby we can easily and quickly manipulate the endogenous human VH region to further explore the regulation and targeting of SHM. This platform will be useful for generating human antibodies with changes in affinity and specificity in vitro.
Importance: An effective immune response requires a highly diverse repertoire of affinity-matured antibodies. Activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) is required for somatic hypermutation (SHM) of immunoglobulin (Ig) genes. Although a great deal has been learned about the regulation of AID, it remains unclear how it is preferentially targeted to particular motifs, to certain locations within the Ig gene and not to other highly expressed genes in the germinal center B cell. This is an important question because AID is highly mutagenic and is sometimes mistargeted to other highly expressed genes, including proto-oncogenes, leading to B cell lymphomas. Here we describe how we utilize recombinase-mediated cassette exchange (RMCE) to modify the sequence of the endogenous heavy chain locus in the Ramos Burkitt's lymphoma cell line. This platform can be used to explore the regulation and targeting of SHM and to generate human antibodies with changes in affinity and specificity in vitro.
Figures

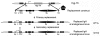

References
-
- Rajewsky K, Förster I, Cumano A. 1987. Evolutionary and somatic selection of the antibody repertoire in the mouse. Science 238:1088–1094 - PubMed
-
- Peled JU, et al. 2008. The biochemistry of somatic hypermutation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 26:481–511 - PubMed
-
- Muramatsu M, et al. 2000. Class switch recombination and hypermutation require activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), a potential RNA editing enzyme. Cell 102:553–563 - PubMed
-
- Revy P, et al. 2000. Activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) deficiency causes the autosomal recessive form of the Hyper-IgM syndrome (HIGM2). Cell 102:565–575 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

