Evidence for regulated interleukin-4 expression in chondrocyte-scaffolds under in vitro inflammatory conditions
- PMID: 21991344
- PMCID: PMC3185011
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025749
Evidence for regulated interleukin-4 expression in chondrocyte-scaffolds under in vitro inflammatory conditions
Abstract
Objective: To elucidate the anti-inflammatory and anabolic effects of regulated expression of IL-4 in chondrocyte-scaffolds under in vitro inflammatory conditions.
Methods: Mature articular chondrocytes from dogs (n = 3) were conditioned through transient transfection using pcDNA3.1.cIL-4 (constitutive) or pCOX-2.cIL-4 (cytokine-responsive) plasmids. Conditioned cells were seeded in alginate microspheres and rat-tail collagen type I matrix (CaReS®) to generate two types of tissue-engineered 3-dimensional scaffolds. Inflammatory arthritis was simulated in the packed chondrocytes through exogenous addition of recombinant canine (rc) IL-1β (100 ng/ml) plus rcTNFα (50 ng/ml) in culture media for 96 hours. Harvested cells and culture media were analyzed by various assays to monitor the anti-inflammatory and regenerative (anabolic) properties of cIL-4.
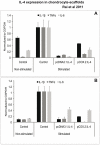
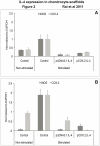
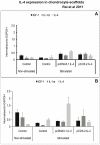
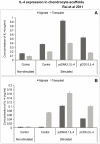
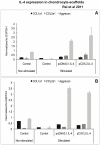
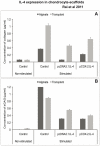
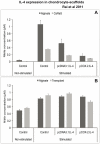
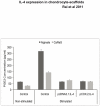
Results: cIL-4 was expressed from COX-2 promoter exclusively on the addition of rcIL-1β and rcTNFα while its expression from CMV promoter was constitutive. The expressed cIL-4 downregulated the mRNA expression of IL-1β, TNFα, IL-6, iNOS and COX-2 in the cells and inhibited the production of NO and PGE(2) in culture media. At the same time, it up-regulated the expression of IGF-1, IL-1ra, COL2a1 and aggrecan in conditioned chondrocytes in both scaffolds along with a diminished release of total collagen and sGAG into the culture media. An increased amount of cIL-4 protein was detected both in chondrocyte cell lysate and in concentrated culture media. Neutralizing anti-cIL-4 antibody assay confirmed that the anti-inflammatory and regenerative effects seen are exclusively driven by cIL-4. There was a restricted expression of IL-4 under COX-2 promoter possibly due to negative feedback loop while it was over-expressed under CMV promoter (undesirable). Furthermore, the anti-inflammatory /anabolic outcomes from both scaffolds were reproducible and the therapeutic effects of cIL-4 were both scaffold- and promoter-independent.
Conclusions: Regulated expression of therapeutic candidate gene(s) coupled with suitable scaffold(s) could potentially serve as a useful tissue-engineering tool to devise future treatment strategies for osteoarthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Pelletier JP, Martel-Pelletier J, Abramson SB. Osteoarthritis, an inflammatory disease: potential implication for the selection of new therapeutic targets. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44:1237–1247. - PubMed
-
- Hegemann N, Wondimu A, Kohn B, Brunnberg L, Schmidt MF. Cytokine profile in canine immune-mediated polyarthritis and osteoarthritis. Vet Comp Orthop Traumatol. 2005;18:67–72. - PubMed
-
- Nuki G. Role of mechanical factors in the aetiology, pathogenesis and progression of osteoarthritis. In: Reginster JY, Pelletier JP, Martel-Pelletier J, Henrotin Y, editors. Osteoarthritis: Clinical and Experimental Aspects. Berlin: Springer-Verlag; 1999. pp. 101–114.
-
- Pelletier JP, Martel-Pelletier J, Howell DS. Etiopathogenesis of osteoarthritis. In: Koopman WJ, editor. Arthritis & Allied Conditions. A Textbook of Rheumatology. 14th ed. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins; 2000. pp. 2195–2245.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

