Immunogenicity of Simulated PCECV Postexposure Booster Doses 1, 3, and 5 Years after 2-Dose and 3-Dose Primary Rabies Vaccination in Schoolchildren
- PMID: 21991438
- PMCID: PMC3170734
- DOI: 10.4061/2011/403201
Immunogenicity of Simulated PCECV Postexposure Booster Doses 1, 3, and 5 Years after 2-Dose and 3-Dose Primary Rabies Vaccination in Schoolchildren
Abstract
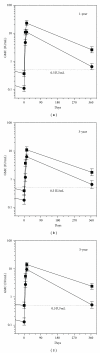
Objectives. To assess the immunogenicity of intradermal (ID) booster doses of Purified Chick Embryo Cell rabies vaccine (PCECV, Rabipur) administered to Thai schoolchildren one, three and five years after a primary ID pre-exposure (PrEP) vaccination series. Methods. In this follow-up study of a randomized, open-label, phase II clinical trial, two simulated post-exposure booster doses of PCECV were administered on days 0 and 3 intradermally to 703 healthy schoolchildren, one, three or five years after primary vaccination with either two or three ID doses of 0.1 mL PCECV. Blood was drawn immediately before and 7, 14 and 365 days after the first booster dose to determine rabies virus neutralizing antibody (RVNA) concentrations. Results. An anamnestic response of approximately 30-fold increase in RVNA concentrations was demonstrated within 14 days after booster. All children (100%) developed adequate RVNA concentrations above 0.5 IU/mL. No vaccine related serious adverse events were seen in any of the vaccinees. Conclusion. ID rabies PrEP with PCECV is safe and immunogenic in schoolchildren and the anamnestic response to a two booster dose vaccination series was found to be adequate one, three, and five years after a two- or three-dose primary PrEP vaccination series.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pre-exposure rabies vaccination using purified chick embryo cell rabies vaccine intradermally is immunogenic and safe.J Pediatr. 2007 Aug;151(2):173-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2007.02.044. J Pediatr. 2007. PMID: 17643772 Clinical Trial.
-
A randomized open-labeled study to demonstrate the non-inferiority of purified chick-embryo cell rabies vaccine administered in the Zagreb regimen (2-1-1) compared with the Essen regimen in Chinese adults.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014;10(10):2805-12. doi: 10.4161/21645515.2014.972773. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014. PMID: 25483635 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Immunogenicity and safety of purified chick-embryo cell rabies vaccine under Zagreb 2-1-1 or 5-dose Essen regimen in Chinese children 6 to 17 years old and adults over 50 years: a randomized open-label study.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015;11(2):435-42. doi: 10.4161/21645515.2014.994460. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015. PMID: 25692350 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) for rabies with purified chick embryo cell vaccine: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2018 Jun;17(6):525-545. doi: 10.1080/14760584.2018.1473765. Epub 2018 Jun 25. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2018. PMID: 29939085 Review.
-
Rabies pre-exposure vaccination of children with purified chick embryo cell vaccine (PCECV).Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2013 Jul;9(7):1454-9. doi: 10.4161/hv.24502. Epub 2013 Apr 9. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2013. PMID: 23571224 Review.
Cited by
-
[Rabies: Prevention strategies for travellers].MMW Fortschr Med. 2020 Jun;162(11):53-58. doi: 10.1007/s15006-020-0576-7. MMW Fortschr Med. 2020. PMID: 32514954 Free PMC article. Review. German.
-
Pre-exposure rabies prophylaxis: a systematic review.Bull World Health Organ. 2017 Mar 1;95(3):210-219C. doi: 10.2471/BLT.16.173039. Epub 2016 Nov 25. Bull World Health Organ. 2017. PMID: 28250534 Free PMC article.
-
Intradermal vaccination for infants and children.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2016 Sep;12(9):2447-55. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2016.1176652. Epub 2016 May 2. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2016. PMID: 27135736 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Quiambao BP, Dimaano EM, Ambas C, Davis R, Banzhoff A, Malerczyk C. Reducing the cost of post-exposure rabies prophylaxis: efficacy of 0.1 ml PCEC rabies vaccine administered intradermally using the Thai Red Cross post-exposure regimen in patients severely exposed to laboratory-confirmed rabid animals. Vaccine. 2005;23(14):1709–1714. - PubMed
-
- WHO. Report No. 931. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO; 2004. WHO expert consultation on Rabies : first report.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

