The Importance of Autonomous Regulation for Students' Successful Translation of Intentions into Behavior Change via Planning
- PMID: 21991441
- PMCID: PMC3170742
- DOI: 10.4061/2011/697856
The Importance of Autonomous Regulation for Students' Successful Translation of Intentions into Behavior Change via Planning
Abstract
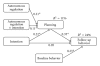
Physical activity has a high prevention potential in adolescents. This study investigated the relations between physical activity and intention, autonomous regulation, and planning. We hypothesized that planning mediates the relationship between intention and behavior and that this mediation should depend on the level of autonomous regulation. Stratified randomization sampling method was administered to assemble a sample of N = 534 students among two schools in China. To test the hypothesis, autonomous regulation, intention, and physical activity were assessed at baseline as well as planning and follow-up physical activity four weeks after the pretest. A moderated mediation model confirmed that planning mediated the intention-behavior relation with the effect of planning being moderated by autonomous regulation. Study results demonstrated that autonomous regulation facilitated the translation of intention into behavior change via planning. To promote physical activity among adolescents, interventions targeting planning and autonomous regulation might facilitate successful translation of intentions into behavior change.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Detrimental Effect of Perceived Controlling Behavior from Physical Education Teachers on Students' Leisure-Time Physical Activity Intentions and Behavior: An Application of the Trans-Contextual Model.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Aug 15;17(16):5939. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17165939. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32824264 Free PMC article.
-
Disentangling the relation between intentions, planning, and behaviour: a moderated mediation analysis.Psychol Health. 2009 Jan;24(1):67-79. doi: 10.1080/08870440801958214. Psychol Health. 2009. PMID: 20186640
-
Planning skills moderate the intention-planning cognitions-behaviour relation: a longitudinal study on physical activity in Chinese adolescents.Res Sports Med. 2013;21(1):12-23. doi: 10.1080/15438627.2012.738441. Res Sports Med. 2013. PMID: 23286419
-
Moderators of the mediated effect of intentions, planning, and saturated-fat intake in obese individuals.Health Psychol. 2012 May;31(3):371-9. doi: 10.1037/a0026497. Epub 2011 Dec 5. Health Psychol. 2012. PMID: 22142278 Clinical Trial.
-
Using action planning to promote exercise behavior.Ann Behav Med. 2010 Aug;40(1):65-76. doi: 10.1007/s12160-010-9190-8. Ann Behav Med. 2010. PMID: 20446124
Cited by
-
Factors that influence planning for physical activity among workers in small- and medium-sized enterprises.Prev Med Rep. 2018 Mar 6;10:150-156. doi: 10.1016/j.pmedr.2018.02.015. eCollection 2018 Jun. Prev Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29868359 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hallal PC, Victora CG, Azevedo MR, Wells JCK. Adolescent physical activity and health: a systematic review. Sports Medicine. 2006;36(12):1019–1030. - PubMed
-
- Kimm SYS, Glynn NW, Obarzanek E, et al. Relation between the changes in physical activity and body-mass index during adolescence: a multicentre longitudinal study. The Lancet. 2005;366(9482):301–307. - PubMed
-
- Reichert FF, Menezes AMB, Wells JCK, Dumith SC, Hallal PC. Physical activity as a predictor of adolescent body fatness: a systematic review. Sports Medicine. 2009;39(4):279–294. - PubMed
-
- Fox KR. The influence of physical activity on mental well-being. Public Health Nutrition. 1999;2(3):411–418. - PubMed
-
- Saxena S, Van Ommeren M, Tang KC, Armstrong TP. Mental health benefits of physical activity. Journal of Mental Health. 2005;14(5):445–451.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

