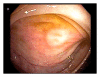
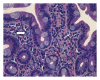
Eosinophilic enterocolitis diagnosed by means of upper endoscopy and colonoscopy with random biopsies treated with budenoside: a case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 21991521
- PMCID: PMC3168459
- DOI: 10.5402/2011/608901
Eosinophilic enterocolitis diagnosed by means of upper endoscopy and colonoscopy with random biopsies treated with budenoside: a case report and review of the literature
Abstract
Intense infiltration of gastrointestinal and colonic mucosa with eosinophils or acidophilic gastroenteritis (EG) is a relatively uncommon picture for a pathologist endoscopist especially outside the pediatric age group and is highly suggestive of an ongoing chronic inflammatory process. Existing literature projected a hypothetical association with allergy but the exact pathophysiology is still unknown. Association with malabsorption, protein losing enteropathy, and refractory ulcers with gastrointestinal bleeding makes the clinical presentation more complicated. We present a unique case of diarrhea and abdominal pain in the clinical presentation with associated peripheral eosinophilia, asthma, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). The patient's symptoms abated after initiation of budesonide.
Figures
References
-
- Rothenberg ME. Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGID) Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 2004;113(1):11–29. - PubMed
-
- Kelly KJ. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition. 2000;30(1):S28–S35. - PubMed
-
- Kaisjer R. Zur Kenntinis der allergischen Affektionen des Verdaungskanals vom Standput des Chrirurgen aus. Arch Klin Chir. 1937;188:36–64.
-
- Guajardo JR, Plotnick LM, Fende JM, Collins MH, Putnam PE, Rothenberg ME. Eosinophil-associated gastrointestinal disorders: a world-wide-web based registry. Journal of Pediatrics. 2002;141(4):576–581. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources