Phamerator: a bioinformatic tool for comparative bacteriophage genomics
- PMID: 21991981
- PMCID: PMC3233612
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-395
Phamerator: a bioinformatic tool for comparative bacteriophage genomics
Abstract
Background: Bacteriophage genomes have mosaic architectures and are replete with small open reading frames of unknown function, presenting challenges in their annotation, comparative analysis, and representation.
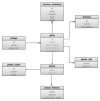
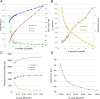
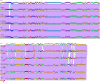
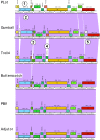
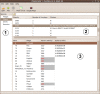
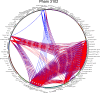
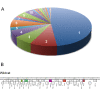
Results: We describe here a bioinformatic tool, Phamerator, that assorts protein-coding genes into phamilies of related sequences using pairwise comparisons to generate a database of gene relationships. This database is used to generate genome maps of multiple phages that incorporate nucleotide and amino acid sequence relationships, as well as genes containing conserved domains. Phamerator also generates phamily circle representations of gene phamilies, facilitating analysis of the different evolutionary histories of individual genes that migrate through phage populations by horizontal genetic exchange.
Conclusions: Phamerator represents a useful tool for comparative genomic analysis and comparative representations of bacteriophage genomes.
Figures

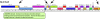
References
-
- Hatfull GF, Pedulla ML, Jacobs-Sera D, Cichon PM, Foley A, Ford ME, Gonda RM, Houtz JM, Hryckowian AJ, Kelchner VA, Namburi S, Pajcini KV, Popovich MG, Schleicher DT, Simanek BZ, Smith AL, Zdanowicz GM, Kumar V, Peebles CL, Jacobs WR Jr, Lawrence JG, Hendrix RW. Exploring the mycobacteriophage metaproteome: phage genomics as an educational platform. PLoS Genet. 2006;2(6):e92. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0020092. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

