HIV-free survival and morbidity among formula-fed infants in a prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV program in rural Haiti
- PMID: 21992146
- PMCID: PMC3220628
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-6405-8-37
HIV-free survival and morbidity among formula-fed infants in a prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV program in rural Haiti
Abstract
Background: Partners In Health (PIH) works with the Ministry of Health to provide comprehensive health services in Haiti. Between 1994 and 2009, PIH recommended exclusive formula feeding in the prevention of mother-to-child transmission (PMTCT) of HIV program and provided support to implement this strategy. We conducted this study to assess HIV-free survival and prevalence of diarrhea and malnutrition among infants in our PMTCT program in rural Haiti where exclusive formula feeding was supported.
Methods: We reviewed medical charts of PMTCT mother-infant pairs at PIH between November 2004 and August 2006 through a retrospective longitudinal study and cross-sectional survey. We performed household surveys for each pair and at control households matched by infant's age and gender.
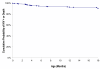
Results: 254 mother-infant pairs were included. 15.3% of infants were low birth weight; most births occurred at home (68.8%). 55.9% of households had no latrine; food insecurity was high (mean score of 18; scale 0-27, SD = 5.3). HIV-free survival at 18 months was 90.6%. Within the cohort, 9 children (3.5%) were HIV-infected and 17 (6.7%) died. Community controls were more likely to be breastfed (P = 0.003) and more likely to introduce food early (P = 0.003) than PMTCT-program households. There was no difference in moderate malnutrition (Z score ≤ 2 SD) between PMTCT and community groups after controlling for guardian's education, marital status, and food insecurity (OR = 1.05; 95% CI: 0.67, 1.64; P = 0.84). Diarrhea was 2.9 times more prevalent among community children than PMTCT infants (30.3% vs. 12.2%; P < 0.0001).
Conclusions: In a PIH-supported program in rural Haiti that addressed socioeconomic barriers to ill-health, breast milk substitution was safe, acceptable and feasible for PMTCT for HIV-infected women choosing this option.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Treatment acceleration program and the experience of the DREAM program in prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV.AIDS. 2007 Jul;21 Suppl 4:S65-71. doi: 10.1097/01.aids.0000279708.09180.f5. AIDS. 2007. PMID: 17620755
-
Breastfeeding by HIV-1-infected women and outcome in their infants: a cohort study from Durban, South Africa.AIDS. 1997 Nov;11(13):1627-33. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199713000-00012. AIDS. 1997. PMID: 9365768
-
HIV-1 Early Infant Diagnosis is an Effective Indicator of the Prevention of Mother-to-Child Transmission Program Performance: Experience from Cameroon.Curr HIV Res. 2015;13(4):286-91. doi: 10.2174/1570162x13666150407143525. Curr HIV Res. 2015. PMID: 25845391
-
Fifteen years of HIV and syphilis outcomes among a prevention of mother-to-child transmission program in Haiti: from monotherapy to Option B.Trop Med Int Health. 2018 Jul;23(7):724-737. doi: 10.1111/tmi.13075. Epub 2018 Jun 14. Trop Med Int Health. 2018. PMID: 29779260
-
Exclusive breastfeeding among HIV exposed infants from birth to 14 weeks of life in Lira, Northern Uganda: a prospective cohort study.Glob Health Action. 2020 Dec 31;13(1):1833510. doi: 10.1080/16549716.2020.1833510. Glob Health Action. 2020. PMID: 33121390 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV: cost-effectiveness of antiretroviral regimens and feeding options in Rwanda.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e54180. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054180. Epub 2013 Feb 20. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23437040 Free PMC article.
-
Retention in Care among HIV-Infected Pregnant Women in Haiti with PMTCT Option B.AIDS Res Treat. 2016;2016:6284290. doi: 10.1155/2016/6284290. Epub 2016 Aug 29. AIDS Res Treat. 2016. PMID: 27651953 Free PMC article.
-
Motor development of infants exposed to maternal human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) but not infected.Int Arch Med. 2013 Oct 31;6(1):45. doi: 10.1186/1755-7682-6-45. Int Arch Med. 2013. PMID: 24171763 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-free survival among breastfed infants born to HIV-positive women in northern Uganda: a facility-based retrospective study.Pan Afr Med J. 2020 Dec 2;37:297. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2020.37.297.22928. eCollection 2020. Pan Afr Med J. 2020. PMID: 33654517 Free PMC article.
-
Disclosure and impact of maternal HIV+ serostatus on mothers and children in rural Haiti.Matern Child Health J. 2014 Dec;18(10):2309-15. doi: 10.1007/s10995-013-1375-x. Matern Child Health J. 2014. PMID: 24158504 Free PMC article.
References
-
- UNAIDS. Global report: UNAIDS report on the global AIDS epidemic 2010. Geneva: UNAIDS; 2010. p. 359.
-
- Dao H, Mofenson LM, Ekpini R, Gilks CF, Barnhart M, Bolu O, Shaffer N. International recommendations on antiretroviral drugs for treatment of HIV-infected women and prevention of mother-to-child HIV transmission in resource-limited settings: 2006 update. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2007;197:S42–55. - PubMed
-
- Thomas T, Masaba R, Borkowf C, Ndivo R, Zeh C, Misore A, Otieno J, Jamieson D, Thigpen M, Bulterys M. et al. Triple-antiretroviral prophylaxis to prevent mother-to-child HIV transmission through breastfeeding-the Kisumu Breastfeeding Study, Kenya: a clinical trial. PLoS Med. 2011;8:e100105. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources