Fast plaque burden assessment of the femoral artery using 3D black-blood MRI and automated segmentation
- PMID: 21992357
- PMCID: PMC3189974
- DOI: 10.1118/1.3633899
Fast plaque burden assessment of the femoral artery using 3D black-blood MRI and automated segmentation
Abstract
Purpose: Vessel wall imaging techniques have been introduced to assess the burden of peripheral arterial disease (PAD) in terms of vessel wall thickness, area or volume. Recent advances in a 3D black-blood MRI sequence known as the 3D motion-sensitized driven equilibrium (MSDE) prepared rapid gradient echo sequence (3D MERGE) have allowed the acquisition of vessel wall images with up to 50 cm coverage, facilitating noninvasive and detailed assessment of PAD. This work introduces an algorithm that combines 2D slice-based segmentation and 3D user editing to allow for efficient plaque burden analysis of the femoral artery images acquired using 3D MERGE.
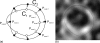
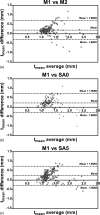
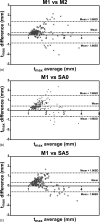
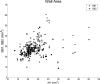
Methods: The 2D slice-based segmentation approach is based on propagating segmentation results of contiguous 2D slices. The 3D image volume was then reformatted using the curved planar reformation (CPR) technique. User editing of the segmented contours was performed on the CPR views taken at different angles. The method was evaluated on six femoral artery images. Vessel wall thickness and area obtained before and after editing on the CPR views were assessed by comparison with manual segmentation. Difference between semiautomatically and manually segmented contours were compared with the difference of the corresponding measurements between two repeated manual segmentations.
Results: The root-mean-square (RMS) errors of the mean wall thickness (t(mean)) and the wall area (WA) of the edited contours were 0.35 mm and 7.1 mm(2), respectively, which are close to the RMS difference between two repeated manual segmentations (RMSE: 0.33 mm in t(mean), 6.6 mm(2) in WA). The time required for the entire semiautomated segmentation process was only 1%-2% of the time required for manual segmentation.
Conclusions: The difference between the boundaries generated by the proposed algorithm and the manually segmented boundary is close to the difference between repeated manual segmentations. The proposed method provides accurate plaque burden measurements, while considerably reducing the analysis time compared to manual review.
Figures








References
-
- Belch J. J. F., Topol E. J., Agnelli G., Bertrand M., Califf R. M., Clement D. L., Creager M. A., Easton J. D., Gavin J. R., Greenland P., Hankey G., Hanrath P., Hirsch A. T., Meyer J., Smith S. C., Sullivan F., and Weber M. A., “Critical issues in peripheral arterial disease detection and management: a call to action.,” Arch. Intern. Med. 163, 884–892 (2003). 10.1001/archinte.163.8.884 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

