Dual inhibition of tumor energy pathway by 2-deoxyglucose and metformin is effective against a broad spectrum of preclinical cancer models
- PMID: 21992792
- PMCID: PMC3237863
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0497
Dual inhibition of tumor energy pathway by 2-deoxyglucose and metformin is effective against a broad spectrum of preclinical cancer models
Abstract
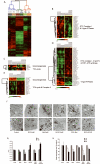
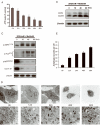
Tumor cell proliferation requires both growth signals and sufficient cellular bioenergetics. The AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway seems dominant over the oncogenic signaling pathway suppressing cell proliferation. This study investigated the preclinical efficacy of targeting the tumor bioenergetic pathway using a glycolysis inhibitor 2-deoxyglucose (2DG) and AMPK agonists, AICAR and metformin. We evaluated the in vitro antitumor activity of 2DG, metformin or AICAR alone, and 2DG in combination either with metformin or AICAR. We examined in vivo efficacy using xenograft mouse models. 2DG alone was not sufficient to promote tumor cell death, reflecting the limited efficacy showed in clinical trials. A combined use of 2DG and AICAR also failed to induce cell death. However, 2DG and metformin led to significant cell death associated with decrease in cellular ATP, prolonged activation of AMPK, and sustained autophagy. Gene expression analysis and functional assays revealed that the selective AMPK agonist AICAR augments mitochondrial energy transduction (OXPHOS) whereas metformin compromises OXPHOS. Importantly, forced energy restoration with methyl pyruvate reversed the cell death induced by 2DG and metformin, suggesting a critical role of energetic deprivation in the underlying mechanism of cell death. The combination of 2DG and metformin inhibited tumor growth in mouse xenograft models. Deprivation of tumor bioenergetics by dual inhibition of energy pathways might be an effective novel therapeutic approach for a broad spectrum of human tumors.
Figures




References
-
- Warburg O. On the origin of cancer cells. Science. 1956;123:309–14. - PubMed
-
- Downey RJ, Akhurst T, Gonen M, Vincent A, Bains MS, Larson S, et al. Preoperative F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography maximal standardized uptake value predicts survival after lung cancer resection. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:3255–60. - PubMed
-
- Gatenby RA, Gillies RJ. Why do cancers have high aerobic glycolysis? Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:891–9. - PubMed
-
- Kumar R, Mavi A, Bural G, Alavi A. Fluorodeoxyglucose-PET in the management of malignant melanoma. Radiol Clin North Am. 2005;43:23–33. - PubMed
-
- DeBerardinis RJ, Lum JJ, Hatzivassiliou G, Thompson CB. The biology of cancer: metabolic reprogramming fuels cell growth and proliferation. Cell Metab. 2008;7:11–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

