A high-resolution map of human evolutionary constraint using 29 mammals
- PMID: 21993624
- PMCID: PMC3207357
- DOI: 10.1038/nature10530
A high-resolution map of human evolutionary constraint using 29 mammals
Abstract
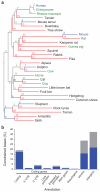
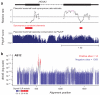
The comparison of related genomes has emerged as a powerful lens for genome interpretation. Here we report the sequencing and comparative analysis of 29 eutherian genomes. We confirm that at least 5.5% of the human genome has undergone purifying selection, and locate constrained elements covering ∼4.2% of the genome. We use evolutionary signatures and comparisons with experimental data sets to suggest candidate functions for ∼60% of constrained bases. These elements reveal a small number of new coding exons, candidate stop codon readthrough events and over 10,000 regions of overlapping synonymous constraint within protein-coding exons. We find 220 candidate RNA structural families, and nearly a million elements overlapping potential promoter, enhancer and insulator regions. We report specific amino acid residues that have undergone positive selection, 280,000 non-coding elements exapted from mobile elements and more than 1,000 primate- and human-accelerated elements. Overlap with disease-associated variants indicates that our findings will be relevant for studies of human biology, health and disease.
Figures


Comment in
-
Comparative genomics: mammalian alignments reveal human functional elements.Nat Rev Genet. 2011 Nov 3;12(12):806-7. doi: 10.1038/nrg3112. Nat Rev Genet. 2011. PMID: 22048660 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lander ES, et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature. 2001;409:860–921. doi:10.1038/35057062. - PubMed
-
- Waterston RH, et al. Initial sequencing and comparative analysis of the mouse genome. Nature. 2002;420:520–562. doi:10.1038/nature01262 nature01262 [pii] - PubMed
-
- Gibbs RA, et al. Genome sequence of the Brown Norway rat yields insights into mammalian evolution. Nature. 2004;428:493–521. doi:10.1038/nature02426 nature02426 [pii] - PubMed
-
- Lindblad-Toh K, et al. Genome sequence, comparative analysis and haplotype structure of the domestic dog. Nature. 2005;438:803–819. doi:nature04338 [pii] 10.1038/nature04338. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

