Gastric infection by Helicobacter pylori
- PMID: 21993716
- PMCID: PMC4531091
- DOI: 10.1007/s11894-011-0226-4
Gastric infection by Helicobacter pylori
Abstract
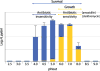
Helicobacter pylori infects half of the world's population and plays a causal role in ulcer disease and gastric cancer. This pathogenic neutralophile uniquely colonizes the acidic gastric milieu through the process of acid acclimation. Acid acclimation is the ability of the organism to maintain periplasmic pH near neutrality in an acidic environment to prevent a fall in cytoplasmic pH in order to maintain viability and growth in acid. Recently, due to an increase in antibiotic resistance, the rate of H. pylori eradication has fallen below 80% generating renewed interest in novel eradication regimens and targets. In this article, we review the gastric biology of H. pylori and acid acclimation, various detection procedures, antibiotic resistance and the role that gastric acidity plays in the susceptibility of the organism to antibiotics currently in use and propose several novel drug targets that would promote eradication in the absence of antibiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Lau JY, Sung J, Hill C, et al. Systematic review of the epidemiology of complicated peptic ulcer disease: incidence, recurrence, risk factors and mortality. Digestion. 2011;84:102–13. - PubMed
-
- Marshall BJ, Warren JR. Unidentified curved bacilli in the stomach of patients with gastritis and peptic ulceration. Lancet. 1984;1:1311–5. - PubMed
-
- Genta RM, Graham DY. Comparison of biopsy sites for the histopathologic diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori: a topographic study of H. pylori density and distribution. Gastrointest Endosc. 1994;40:342–5. - PubMed
-
- Baumgartner HK, Montrose MH. Regulated alkali secretion acts in tandem with unstirred layers to regulate mouse gastric surface pH. Gastroenterology. 2004;126:774–83. - PubMed
-
- Henriksnas J, Phillipson M, Storm M, et al. Impaired mucus-bicarbonate barrier in Helicobacter pylori-infected mice. Am J Physiol. 2006;291:G396–403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

