Cytokine induction of tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 is mediated by STAT3 in colon cancer cells
- PMID: 21994466
- PMCID: PMC3243771
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-10-0210
Cytokine induction of tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 is mediated by STAT3 in colon cancer cells
Abstract
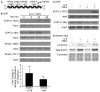
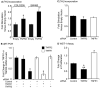
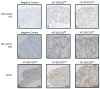
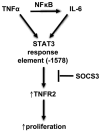
The IL-6/STAT3 and TNFα/NFκB pathways are emerging as critical mediators of inflammation-associated colon cancer. TNF receptor (TNFR) 2 expression is increased in inflammatory bowel diseases, the azoxymethane/dextran sodium sulfate (AOM/DSS) model of colitis-associated cancer, and by combined interleukin (IL) 6 and TNFα. The molecular mechanisms that regulate TNFR2 remain undefined. This study used colon cancer cell lines to test the hypothesis that IL-6 and TNFα induce TNFR2 via STAT3 and/or NFκB. Basal and IL-6 + TNFα-induced TNFR2 were decreased by pharmacologic STAT3 inhibition. NFκB inhibition had little effect on IL-6 + TNFα-induced TNFR2, but did inhibit induction of endogenous IL-6 and TNFR2 in cells treated with TNFα alone. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) revealed cooperative effects of IL-6 + TNFα to induce STAT3 binding to a -1,578 STAT response element in the TNFR2 promoter but no effect on NFκB binding to consensus sites. Constitutively active STAT3 was sufficient to induce TNFR2 expression. Overexpression of SOCS3, a cytokine-inducible STAT3 inhibitor, which reduces tumorigenesis in preclinical models of colitis-associated cancer, decreased cytokine-induced TNFR2 expression and STAT3 binding to the -1,578 STAT response element. SOCS3 overexpression also decreased proliferation of colon cancer cells and dramatically decreased anchorage-independent growth of colon cancer cells, even cells overexpressing TNFR2. Collectively, these studies show that IL-6- and TNFα-induced TNFR2 expression in colon cancer cells is mediated primarily by STAT3 and provide evidence that TNFR2 may contribute to the tumor-promoting roles of STAT3.
Figures



References
-
- Ekbom A, Helmick C, Zack M, Adami HO. Ulcerative colitis and colorectal cancer. A population-based study. N Engl J Med. 1990;323:1228–33. - PubMed
-
- Ekbom A, Helmick C, Zack M, Adami HO. Increased risk of large-bowel cancer in Crohn's disease with colonic involvement. Lancet. 1990;336:357–9. - PubMed
-
- Munkholm P. Review article: the incidence and prevalence of colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel disease. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 2003;18 2:1–5. - PubMed
-
- Becker C, Fantini MC, Wirtz S, Nikolaev A, Lehr HA, Galle PR, Rose-John S, Neurath MF. IL-6 signaling promotes tumor growth in colorectal cancer. CellCycle. 2005;4:217–20. - PubMed
-
- Corvinus FM, Orth C, Moriggl R, Tsareva SA, Wagner S, Pfitzner EB, Baus D, Kaufmann R, Huber LA, Zatloukal K, Beug H, Ohlschlager P, Schutz A, Halbhuber KJ, Friedrich K. Persistent STAT3 activation in colon cancer is associated with enhanced cell proliferation and tumor growth. Neoplasia (New York, NY) 2005;7:545–55. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

