Local connections of layer 5 GABAergic interneurons to corticospinal neurons
- PMID: 21994491
- PMCID: PMC3182329
- DOI: 10.3389/fncir.2011.00012
Local connections of layer 5 GABAergic interneurons to corticospinal neurons
Abstract
In the local circuit of the cerebral cortex, GABAergic inhibitory interneurons are considered to work in collaboration with excitatory neurons. Although many interneuron subgroups have been described in the cortex, local inhibitory connections of each interneuron subgroup are only partially understood with respect to the functional neuron groups that receive these inhibitory connections. In the present study, we morphologically examined local inhibitory inputs to corticospinal neurons (CSNs) in motor areas using transgenic rats in which GABAergic neurons expressed fluorescent protein Venus. By analysis of biocytin-filled axons obtained with whole-cell recording/staining in cortical slices, we classified fast-spiking (FS) neurons in layer (L) 5 into two types, FS1 and FS2, by their high and low densities of axonal arborization, respectively. We then investigated the connections of FS1, FS2, somatostatin (SOM)-immunopositive, and other (non-FS/non-SOM) interneurons to CSNs that were retrogradely labeled in motor areas. When close appositions between the axon boutons of the intracellularly labeled interneurons and the somata/dendrites of the retrogradely labeled CSNs were examined electron-microscopically, 74% of these appositions made symmetric synaptic contacts. The axon boutons of single FS1 neurons were two- to fourfold more frequent in appositions to the somata/dendrites of CSNs than those of FS2, SOM, and non-FS/non-SOM neurons. Axosomatic appositions were most frequently formed with axon boutons of FS1 and FS2 neurons (approximately 30%) and least frequently formed with those of SOM neurons (7%). In contrast, SOM neurons most extensively sent axon boutons to the apical dendrites of CSNs. These results might suggest that motor outputs are controlled differentially by the subgroups of L5 GABAergic interneurons in cortical motor areas.
Keywords: FS neuron; apposition; corticospinal neuron; inhibitory; morphology; motor areas; somatostatin-immunopositive neuron; synapse.
Figures
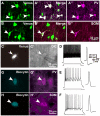
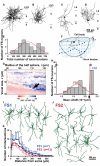
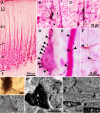
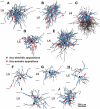


Similar articles
-
Local connections of excitatory neurons in motor-associated cortical areas of the rat.Front Neural Circuits. 2013 May 28;7:75. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2013.00075. eCollection 2013. Front Neural Circuits. 2013. PMID: 23754982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Axo-axonic synapses formed by somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in rat and monkey visual cortex.J Comp Neurol. 2002 Jan 28;443(1):1-14. doi: 10.1002/cne.1425. J Comp Neurol. 2002. PMID: 11793343
-
Preprodynorphin-expressing neurons constitute a large subgroup of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic interneurons in the mouse neocortex.J Comp Neurol. 2014 May 1;522(7):1506-26. doi: 10.1002/cne.23477. J Comp Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24122731
-
Local Connections of Pyramidal Neurons to Parvalbumin-Producing Interneurons in Motor-Associated Cortical Areas of Mice.eNeuro. 2022 Feb 2;9(1):ENEURO.0567-20.2021. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0567-20.2021. Print 2022 Jan-Feb. eNeuro. 2022. PMID: 34965927 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple axon collaterals of single corticospinal axons in the cat spinal cord.J Neurophysiol. 1986 Mar;55(3):425-48. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.55.3.425. J Neurophysiol. 1986. PMID: 3514812 Review.
Cited by
-
Intrinsic electrophysiology of mouse corticospinal neurons: a class-specific triad of spike-related properties.Cereb Cortex. 2013 Aug;23(8):1965-77. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhs184. Epub 2012 Jul 3. Cereb Cortex. 2013. PMID: 22761308 Free PMC article.
-
Corticospinal neurons from motor and somatosensory cortices exhibit different temporal activity dynamics during motor learning.Front Hum Neurosci. 2022 Nov 25;16:1043501. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2022.1043501. eCollection 2022. Front Hum Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36504625 Free PMC article.
-
Local connections of excitatory neurons in motor-associated cortical areas of the rat.Front Neural Circuits. 2013 May 28;7:75. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2013.00075. eCollection 2013. Front Neural Circuits. 2013. PMID: 23754982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Motor cortex microcircuit simulation based on brain activity mapping.Neural Comput. 2014 Jul;26(7):1239-62. doi: 10.1162/NECO_a_00602. Epub 2014 Apr 7. Neural Comput. 2014. PMID: 24708371 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of Midbrain Dopamine Neurons Does Not Alter GABAergic Inhibition Mediated by Parvalbumin-Expressing Interneurons in Mouse Primary Motor Cortex.eNeuro. 2024 May 9;11(5):ENEURO.0010-24.2024. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0010-24.2024. Print 2024 May. eNeuro. 2024. PMID: 38658137 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bayraktar T., Staiger J. F., Acsady L., Cozzari C., Freund T. F., Zilles K. (1997). Co-localization of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, gamma-aminobutyric acid and choline acetyltransferase in neocortical interneurons of the adult rat. Brain Res. 757, 209–21710.1016/S0006-8993(97)00218-7 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

