HIV-1 Ribonuclease H: Structure, Catalytic Mechanism and Inhibitors
- PMID: 21994660
- PMCID: PMC3185654
- DOI: 10.3390/v2040900
HIV-1 Ribonuclease H: Structure, Catalytic Mechanism and Inhibitors
Abstract
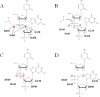
Since the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) was discovered as the etiological agent of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), it has encouraged much research into antiviral compounds. The reverse transcriptase (RT) of HIV has been a main target for antiviral drugs. However, all drugs developed so far inhibit the polymerase function of the enzyme, while none of the approved antiviral agents inhibit specifically the necessary ribonuclease H (RNase H) function of RT. This review provides a background on structure-function relationships of HIV-1 RNase H, as well as an outline of current attempts to develop novel, potent chemotherapeutics against a difficult drug target.
Keywords: HIV; RNase H; drug resistance; inhibitors; reverse transcriptase.
Figures

References
-
- Telesnitsky A, Goff S. Retroviruses. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA: 1997. pp. 121–160.
-
- De Clercq E. Anti-HIV drugs: 25 compounds approved within 25 years after the discovery of HIV. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2009;33:307–320. - PubMed
-
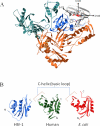
- Davies JF, 2nd, Hostomska Z, Hostomsky Z, Jordan SR, Matthews DA. Crystal structure of the ribonuclease H domain of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Science. 1991;252:88–95. - PubMed
-
- Ding J, Das K, Hsiou Y, Sarafianos SG, Clark AD, Jr, Jacobo-Molina A, Tantillo C, Hughes SH, Arnold E. Structure and functional implications of the polymerase active site region in a complex of HIV-1 RT with a double-stranded DNA template-primer and an antibody Fab fragment at 2.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1998;284:1095–1111. - PubMed
-
- Huang H, Chopra R, Verdine GL, Harrison SC. Structure of a covalently trapped catalytic complex of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase: implications for drug resistance. Science. 1998;282:1669–1675. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

