Increased interleukin-6 activity associated with painful chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in women after breast cancer treatment
- PMID: 21994811
- PMCID: PMC3168945
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/281531
Increased interleukin-6 activity associated with painful chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in women after breast cancer treatment
Abstract
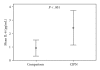
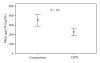
Accumulating evidence suggests that neural-immune interactions are involved in the development of painful chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, particularly through the increased release of proinflammatory cytokines. The purpose of this study was used to evaluate levels of interleukin [IL]-6 and IL-6 receptors in women with breast cancer after the conclusion of chemotherapy who either had painful symptoms of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN group, N = 20) or did not experience CIPN symptoms (Comparison group, N = 20). CIPN participants had significantly higher levels of IL-6 and soluble IL-6R (sIL-6R) compared to women without CIPN symptoms (P < .001 for both). In addition, soluble gp130, which blocks the IL-6/sIL-6R complex from binding to gp130 within the cellular membrane, was significantly lower (P < .01). Circulating concentrations of sIL-6R were inversely correlated with the density of IL-6R on the cell surface of monocytes in the total sample (r = -.614, P = .005). These findings suggest that IL-6 transsignaling may be an important biological mechanism associated with the persistence of painful CIPN symptoms, with potential implications for symptom management and research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Soluble gp130 is the natural inhibitor of soluble interleukin-6 receptor transsignaling responses.Eur J Biochem. 2001 Jan;268(1):160-7. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.2001.01867.x. Eur J Biochem. 2001. PMID: 11121117
-
The soluble form of the IL-6 receptor (sIL-6R alpha) is a potent growth factor for AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) cells; the soluble form of gp130 is antagonistic for sIL-6R alpha-induced AIDS-KS cell growth.Int Immunol. 1996 Apr;8(4):595-602. doi: 10.1093/intimm/8.4.595. Int Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8722639
-
Circulating interleukin 6 and soluble forms of its receptors in relation to resting energy expenditure in women with anorexia nervosa.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2013 Dec;79(6):812-6. doi: 10.1111/cen.12118. Epub 2013 May 6. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2013. PMID: 23199226
-
IL-6 transsignaling: the in vivo consequences.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2005 May;25(5):241-53. doi: 10.1089/jir.2005.25.241. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2005. PMID: 15871661 Review.
-
The role of transsignalling via the agonistic soluble IL-6 receptor in human diseases.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 Nov 11;1592(3):323-43. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(02)00325-7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. PMID: 12421676 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphosulindac (OXT-328) prevents and reverses chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy in mice.Front Neurosci. 2024 Jan 29;17:1240372. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1240372. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38347876 Free PMC article.
-
Pain and inflammation in women with early-stage breast cancer prior to induction of chemotherapy.Biol Res Nurs. 2013 Apr;15(2):234-41. doi: 10.1177/1099800411425857. Epub 2011 Nov 14. Biol Res Nurs. 2013. PMID: 22084403 Free PMC article.
-
Ion channels and neuronal hyperexcitability in chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy; cause and effect?Mol Pain. 2017 Jan-Dec;13:1744806917714693. doi: 10.1177/1744806917714693. Mol Pain. 2017. PMID: 28580836 Free PMC article.
-
Symptoms of anxiety but not depression before start of taxane-based chemotherapy are associated with peripheral neuropathy: a multicenter study in women with breast cancer.Support Care Cancer. 2022 Aug;30(8):6947-6953. doi: 10.1007/s00520-022-07093-4. Epub 2022 May 11. Support Care Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35543818 Free PMC article.
-
Chemokine Signaling in Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathic Pain.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 14;20(12):2904. doi: 10.3390/ijms20122904. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31197114 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Armstrong T, Almadrones L, Gilbert MR. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Oncology Nursing Forum. 2005;32(2):305–311. - PubMed
-
- Paice JA. Clinical challenges: chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Seminars in Oncology Nursing. 2009;25(2):S8–S19. - PubMed
-
- Polomano RC, Farrar JT. Pain and neuropathy in cancer survivors. American Journal of Nursing. 2006;106(3):39–47. - PubMed
-
- Visovsky C, Daly BJ. Clinical evaluation and patterns of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Journal of the American Academy of Nurse Practitioners. 2004;16(8):353–359. - PubMed
-
- Bhagra A, Rao RD. Chemotheraphy-induced neuropathy. Current Oncology Reports. 2007;9(4):290–299. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

