Capturing a fusion intermediate of influenza hemagglutinin with a cholesterol-conjugated peptide, a new antiviral strategy for influenza virus
- PMID: 21994935
- PMCID: PMC3234914
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.254243
Capturing a fusion intermediate of influenza hemagglutinin with a cholesterol-conjugated peptide, a new antiviral strategy for influenza virus
Abstract
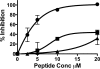
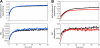
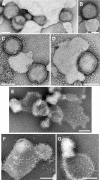
We previously described fusion-inhibitory peptides that are targeted to the cell membrane by cholesterol conjugation and potently inhibit enveloped viruses that fuse at the cell surface, including HIV, parainfluenza, and henipaviruses. However, for viruses that fuse inside of intracellular compartments, fusion-inhibitory peptides have exhibited very low antiviral activity. We propose that for these viruses, too, membrane targeting via cholesterol conjugation may yield potent compounds. Here we compare the activity of fusion-inhibitory peptides derived from the influenza hemagglutinin (HA) and show that although the unconjugated peptides are inactive, the cholesterol-conjugated compounds are effective inhibitors of infectivity and membrane fusion. We hypothesize that the cholesterol moiety, by localizing the peptides to the target cell membrane, allows the peptides to follow the virus to the intracellular site of fusion. The cholesterol-conjugated peptides trap HA in a transient intermediate state after fusion is triggered but before completion of the refolding steps that drive the merging of the viral and cellular membranes. These results provide proof of concept for an antiviral strategy that is applicable to intracellularly fusing viruses, including known and emerging viral pathogens.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01AI31971/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R00 GM080352/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54AI057158/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EB011707/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI076335/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21EB011707/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AI057158/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS076385/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21AI090354/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R00GM080352/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI031971/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI076335/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI090354/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K99 GM080352/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

