Assessment of bias for MRI diffusion tensor imaging using SIMEX
- PMID: 21995019
- PMCID: PMC3197727
- DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-23629-7_14
Assessment of bias for MRI diffusion tensor imaging using SIMEX
Abstract
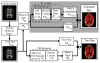
Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) is a Magnetic Resonance Imaging method for measuring water diffusion in vivo. One powerful DTI contrast is fractional anisotropy (FA). FA reflects the strength of water's diffusion directional preference and is a primary metric for neuronal fiber tracking. As with other DTI contrasts, FA measurements are obscured by the well established presence of bias. DTI bias has been challenging to assess because it is a multivariable problem including SNR, six tensor parameters, and the DTI collection and processing method used. SIMEX is a modem statistical technique that estimates bias by tracking measurement error as a function of added noise. Here, we use SIMEX to assess bias in FA measurements and show the method provides; i) accurate FA bias estimates, ii) representation of FA bias that is data set specific and accessible to non-statisticians, and iii) a first time possibility for incorporation of bias into DTI data analysis.
Figures



References
-
- Le Bihan D, van Zijl P. From the diffusion coefficient to the diffusion tensor. NMR Biomed. 2002;15:431–434. - PubMed
-
- Farrell JA, Landman BA, Jones CK, Smith SA, Prince JL, van Zijl PC, Mori S. Effects of signal-to-noise ratio on the accuracy and reproducibility of diffusion tensor imaging-derived fractional anisotropy, mean diffusivity, and principal eigenvector measurements at 1.5 T. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2007;26:756–767. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jones DK, Basser PJ. “Squashing peanuts and smashing pumpkins”: How noise distorts diffusion-weighted MR data. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2004;52:979–993. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
