Derivation and characterization of embryonic stem cells lines derived from transgenic Fischer 344 and Dark Agouti rats
- PMID: 21995453
- PMCID: PMC3359639
- DOI: 10.1089/scd.2011.0370
Derivation and characterization of embryonic stem cells lines derived from transgenic Fischer 344 and Dark Agouti rats
Abstract
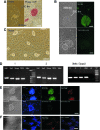
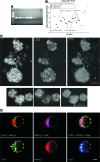
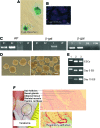
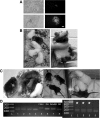
Rat embryonic stem cell (ESC) lines are not widely available, and there are only 2 lines available for distribution. Here, ESC lines were derived and characterized from Fischer 344 (F344) rats that express marker transgenes either β-galactosidase or human placental alkaline phosphatase (AP), nontransgenic F344 rats, and from Dark Agouti (DA) rats. The ESC lines were maintained in an undifferentiated state as characterized by colony morphology, expression of Oct4, Nanog, Sox-2, Cdx2, and Stella, staining for AP, and stage-specific embryonic antigen-1. Pluripotency was demonstrated in vitro by differentiation to embryoid bodies, followed by embryonic monsters. The Cdx2 expression by ESCs was unexpected and was confirmed via reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction, immunocytochemistry. Pluripotency of ESCs was demonstrated in vivo by production of teratoma after an injection into F344 nontransgenic rats, and by an injection of male DA ESCs into F344 or Sprague-Dawley rat blastocysts and the generation of chimeric rats and germline contribution. ESCs from both F344 and DA contributed to chimeric rats, and one DA ESC line was proved to be germline competent. ESC sublines were created by transfection with a plasmid expressing enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP) under the control of a beta actin promoter and cytomegalovirus enhancer (pCX-eGFP) or by transfection with a plasmid expressing GFP under the control of a 3.1 kb portion of the rat Oct4 promoter (pN1-Oct4-GFP). In pN1-Oct4-GFP sublines, GFP gene expression and fluorescence were shown to be correlated with endogenous Oct4 gene expression. Therefore, these new ESC lines may be useful for tissue engineering and transplantation studies or for optimizing culture conditions required for self-renewal and differentiation of rat ESCs. While they made chimeric rats, further work is needed to confirm whether the transgenic F344 rat ESCs described here are germline-competent ESCs.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Derivation of a germline competent transgenic Fischer 344 embryonic stem cell line.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56518. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056518. Epub 2013 Feb 20. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23437152 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of high-level stable transgene expressing human embryonic stem cell lines using Chinese hamster elongation factor-1 alpha promoter system.Stem Cells Dev. 2008 Aug;17(4):825-36. doi: 10.1089/scd.2007.0233. Stem Cells Dev. 2008. PMID: 18788934
-
Germline transmission of a novel rat embryonic stem cell line derived from transgenic rats.Stem Cells Dev. 2012 Sep 20;21(14):2606-12. doi: 10.1089/scd.2012.0040. Epub 2012 May 4. Stem Cells Dev. 2012. PMID: 22455749 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering the true identity of naïve pluripotent stem cells.Trends Cell Biol. 2013 Sep;23(9):442-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2013.04.004. Epub 2013 May 17. Trends Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23685019 Review.
-
Immunogenicity of embryonic stem cell-derived progenitors after transplantation.Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2011 Feb;16(1):90-5. doi: 10.1097/MOT.0b013e3283424faa. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2011. PMID: 21150615 Review.
Cited by
-
From engineering to editing the rat genome.Mamm Genome. 2017 Aug;28(7-8):302-314. doi: 10.1007/s00335-017-9705-8. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Mamm Genome. 2017. PMID: 28752194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proof of pluripotency of rat iPSCs missing.Cell Prolif. 2013 Apr;46(2):119-20. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12025. Cell Prolif. 2013. PMID: 23510465 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Derivation of embryonic stem cell lines from parthenogenetically developing rat blastocysts.Stem Cells Dev. 2014 Jan 15;23(2):107-14. doi: 10.1089/scd.2013.0200. Epub 2013 Nov 7. Stem Cells Dev. 2014. PMID: 24010570 Free PMC article.
-
Positron emission tomography based in-vivo imaging of early phase stem cell retention after intramyocardial delivery in the mouse model.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013 Oct;40(11):1730-8. doi: 10.1007/s00259-013-2480-1. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013. PMID: 23860738
-
Derivation of a germline competent transgenic Fischer 344 embryonic stem cell line.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56518. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056518. Epub 2013 Feb 20. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23437152 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

