Internal control genes for quantitative RT-PCR expression analysis in mouse osteoblasts, osteoclasts and macrophages
- PMID: 21996334
- PMCID: PMC3204251
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-0500-4-410
Internal control genes for quantitative RT-PCR expression analysis in mouse osteoblasts, osteoclasts and macrophages
Abstract
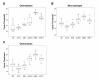
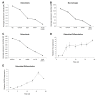
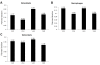
Background: Real-time quantitative RT-PCR (qPCR) is a powerful technique capable of accurately quantitating mRNA expression levels over a large dynamic range. This makes qPCR the most widely used method for studying quantitative gene expression. An important aspect of qPCR is selecting appropriate controls or normalization factors to account for any differences in starting cDNA quantities between samples during expression studies. Here, we report on the selection of a concise set of housekeeper genes for the accurate normalization of quantitative gene expression data in differentiating osteoblasts, osteoclasts and macrophages. We implemented the use of geNorm, an algorithm that determines the suitability of genes to function as housekeepers by assessing expression stabilities. We evaluated the expression stabilities of 18S, ACTB, B2M, GAPDH, HMBS and HPRT1 genes.
Findings: Our analyses revealed that 18S and GAPDH were regulated during osteoblast differentiation and are not suitable for use as reference genes. The most stably expressed genes in osteoblasts were ACTB, HMBS and HPRT1 and their geometric average constitutes a suitable normalization factor upon which gene expression data can be normalized. In macrophages, 18S and GAPDH were the most variable genes while HMBS and B2M were the most stably expressed genes. The geometric average of HMBS and B2M expression levels forms a suitable normalization factor to account for potential differences in starting cDNA quantities during gene expression analysis in macrophages. The expression stabilities of the six candidate reference genes in osteoclasts were, on average, more variable than that observed in macrophages but slightly less variable than those seen in osteoblasts. The two most stably expressed genes in osteoclasts were HMBS and B2M and the genes displaying the greatest levels of variability were 18S and GAPDH. Notably, 18S and GAPDH were the two most variably expressed control genes in all three cell types. The geometric average of HMBS, B2M and ACTB creates an appropriate normalization factor for gene expression studies in osteoclasts.
Conclusion: We have identified concise sets of genes suitable to use as normalization factors for quantitative real-time RT-PCR gene expression studies in osteoblasts, osteoclasts and macrophages.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

