A novel approach of homozygous haplotype sharing identifies candidate genes in autism spectrum disorder
- PMID: 21996756
- PMCID: PMC3303079
- DOI: 10.1007/s00439-011-1094-6
A novel approach of homozygous haplotype sharing identifies candidate genes in autism spectrum disorder
Abstract
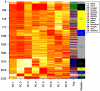
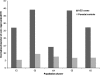
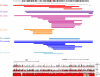
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a highly heritable disorder of complex and heterogeneous aetiology. It is primarily characterized by altered cognitive ability including impaired language and communication skills and fundamental deficits in social reciprocity. Despite some notable successes in neuropsychiatric genetics, overall, the high heritability of ASD (~90%) remains poorly explained by common genetic risk variants. However, recent studies suggest that rare genomic variation, in particular copy number variation, may account for a significant proportion of the genetic basis of ASD. We present a large scale analysis to identify candidate genes which may contain low-frequency recessive variation contributing to ASD while taking into account the potential contribution of population differences to the genetic heterogeneity of ASD. Our strategy, homozygous haplotype (HH) mapping, aims to detect homozygous segments of identical haplotype structure that are shared at a higher frequency amongst ASD patients compared to parental controls. The analysis was performed on 1,402 Autism Genome Project trios genotyped for 1 million single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). We identified 25 known and 1,218 novel ASD candidate genes in the discovery analysis including CADM2, ABHD14A, CHRFAM7A, GRIK2, GRM3, EPHA3, FGF10, KCND2, PDZK1, IMMP2L and FOXP2. Furthermore, 10 of the previously reported ASD genes and 300 of the novel candidates identified in the discovery analysis were replicated in an independent sample of 1,182 trios. Our results demonstrate that regions of HH are significantly enriched for previously reported ASD candidate genes and the observed association is independent of gene size (odds ratio 2.10). Our findings highlight the applicability of HH mapping in complex disorders such as ASD and offer an alternative approach to the analysis of genome-wide association data.
Figures

References
-
- Benko S, Fantes JA, Amiel J, Kleinjan DJ, Thomas S, Ramsay J, Jamshidi N, Essafi A, Heaney S, Gordon CT, McBride D, Golzio C, Fisher M, Perry P, Abadie V, Ayuso C, Holder-Espinasse M, Kilpatrick N, Lees MM, Picard A, Temple IK, Thomas P, Vazquez MP, Vekemans M, Roest Crollius H, Hastie ND, Munnich A, Etchevers HC, Pelet A, Farlie PG, Fitzpatrick DR, Lyonnet S. Highly conserved non-coding elements on either side of SOX9 associated with Pierre Robin sequence. Nat Genet. 2009;41:359–364. doi: 10.1038/ng.329. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 NS049261/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS049261/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS026630/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD055751/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD055784/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 090532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MH06359/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- G0601030/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U54 MH066673/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HD055751/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- MH57881/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD055782/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U24 MH081810/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HD035465/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- MH066673/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH057881/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- AS2482/AS/Autism Speaks/United States
- 075491/Z/04/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MH55284/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH080647/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH061009/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HD055782/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH061009/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH081754/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH065215/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- 1U24MH081810/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U10 MH066766/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS042165/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MH66766/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH52708/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH057881/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- NS042165/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH080647/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HD055784/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH081754/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH055284/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- NS026630/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HD35465/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

