An active contour method for bone cement reconstruction from C-arm x-ray images
- PMID: 21997251
- PMCID: PMC4451112
- DOI: 10.1109/TMI.2011.2171498
An active contour method for bone cement reconstruction from C-arm x-ray images
Abstract
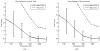
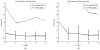
A novel algorithm is presented to segment and reconstruct injected bone cement from a sparse set of X-ray images acquired at arbitrary poses. The sparse X-ray multi-view active contour (SxMAC-pronounced "smack") can 1) reconstruct objects for which the background partially occludes the object in X-ray images, 2) use X-ray images acquired on a noncircular trajectory, and 3) incorporate prior computed tomography (CT) information. The algorithm's inputs are preprocessed X-ray images, their associated pose information, and prior CT, if available. The algorithm initiates automated reconstruction using visual hull computation from a sparse number of X-ray images. It then improves the accuracy of the reconstruction by optimizing a geodesic active contour. Experiments with mathematical phantoms demonstrate improvements over a conventional silhouette based approach, and a cadaver experiment demonstrates SxMAC's ability to reconstruct high contrast bone cement that has been injected into a femur and achieve sub-millimeter accuracy with four images.
Figures












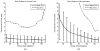
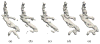
Similar articles
-
Low-dose CT reconstruction method based on prior information of normal-dose image.J Xray Sci Technol. 2020;28(6):1091-1111. doi: 10.3233/XST-200716. J Xray Sci Technol. 2020. PMID: 33044223
-
Quantitative evaluation of a cone-beam computed tomography-planning computed tomography deformable image registration method for adaptive radiation therapy.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2007 Nov 5;8(4):96-113. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v8i4.2432. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2007. PMID: 18449149 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetric impact of image artifact from a wide-bore CT scanner in radiotherapy treatment planning.Med Phys. 2011 Jul;38(7):4451-63. doi: 10.1118/1.3604150. Med Phys. 2011. PMID: 21859046
-
Line Integral Alternating Minimization Algorithm for Dual-Energy X-Ray CT Image Reconstruction.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2016 Feb;35(2):685-98. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2015.2490658. Epub 2015 Oct 14. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2016. PMID: 26469126 Free PMC article.
-
Fluoroscopy-based 3-D reconstruction of femoral bone cement: a new approach for revision total hip replacement.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2005 Apr;52(4):664-75. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2005.844032. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2005. PMID: 15825868
Cited by
-
Improved algorithm for gradient vector flow based active contour model using global and local information.ScientificWorldJournal. 2013 Sep 24;2013:479675. doi: 10.1155/2013/479675. eCollection 2013. ScientificWorldJournal. 2013. PMID: 24223506 Free PMC article.
-
A Particle Model for Prediction of Cement Infiltration of Cancellous Bone in Osteoporotic Bone Augmentation.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 26;8(6):e67958. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067958. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23840794 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Garfin SR, Yuan HA, Reiley MA. New technologies in spine: Kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty for the treatment of painful osteoporotic compression fractures. Spine. 2001;26:1511. - PubMed
-
- Beckmann J, Ferguson S, Gebauer M, Luering C, Gasser B, Heini P. Femoroplasty-augmentation of the proximal femur with a composite bone cement-feasibility, biomechanical properties and osteosynthesis potential. Med Eng Phys. 2007;29:755–764. - PubMed
-
- Otake Y, Armand M, Sadowsky O, Armiger R, Kutzer M, Mears S, Kazanzides P, Taylor R. An image-guided femoroplasty system: Development and initial cadaver studies. Proc. SPIE; San Diego, CA. 2010. p. 76250P.

