An active contour method for bone cement reconstruction from C-arm x-ray images
- PMID: 21997251
- PMCID: PMC4451112
- DOI: 10.1109/TMI.2011.2171498
An active contour method for bone cement reconstruction from C-arm x-ray images
Abstract
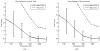
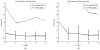
A novel algorithm is presented to segment and reconstruct injected bone cement from a sparse set of X-ray images acquired at arbitrary poses. The sparse X-ray multi-view active contour (SxMAC-pronounced "smack") can 1) reconstruct objects for which the background partially occludes the object in X-ray images, 2) use X-ray images acquired on a noncircular trajectory, and 3) incorporate prior computed tomography (CT) information. The algorithm's inputs are preprocessed X-ray images, their associated pose information, and prior CT, if available. The algorithm initiates automated reconstruction using visual hull computation from a sparse number of X-ray images. It then improves the accuracy of the reconstruction by optimizing a geodesic active contour. Experiments with mathematical phantoms demonstrate improvements over a conventional silhouette based approach, and a cadaver experiment demonstrates SxMAC's ability to reconstruct high contrast bone cement that has been injected into a femur and achieve sub-millimeter accuracy with four images.
Figures












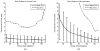
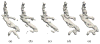
References
-
- Garfin SR, Yuan HA, Reiley MA. New technologies in spine: Kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty for the treatment of painful osteoporotic compression fractures. Spine. 2001;26:1511. - PubMed
-
- Beckmann J, Ferguson S, Gebauer M, Luering C, Gasser B, Heini P. Femoroplasty-augmentation of the proximal femur with a composite bone cement-feasibility, biomechanical properties and osteosynthesis potential. Med Eng Phys. 2007;29:755–764. - PubMed
-
- Otake Y, Armand M, Sadowsky O, Armiger R, Kutzer M, Mears S, Kazanzides P, Taylor R. An image-guided femoroplasty system: Development and initial cadaver studies. Proc. SPIE; San Diego, CA. 2010. p. 76250P.

