Protein kinase C-beta inhibition induces apoptosis and inhibits cell cycle progression in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-related non-hodgkin lymphoma cells
- PMID: 21997316
- PMCID: PMC3246133
- DOI: 10.2310/JIM.0b013e318237eb55
Protein kinase C-beta inhibition induces apoptosis and inhibits cell cycle progression in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-related non-hodgkin lymphoma cells
Abstract
Introduction: Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)-related non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) constitutes an aggressive variety of lymphomas characterized by increased extranodal involvement, relapse rate, and resistance to chemotherapy. Protein kinase C-beta (PKCβ) targeting showed promising results in preclinical and clinical studies involving a wide variety of cancers, but studies describing the role of PKCβ in AIDS-NHL are primitive if not lacking.
Methods: In the present study, 3 AIDS-NHL cell lines were examined: 2F7 (AIDS-Burkitt lymphoma), BCBL-1 (AIDS-primary effusion lymphoma), and UMCL01-101 (AIDS-diffuse large B-cell lymphoma).
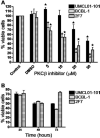
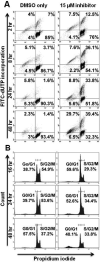
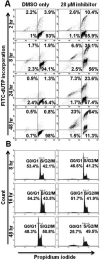
Results: Immunoblot analysis demonstrated expression of PKCβ1 and PKCβ2 in 2F7 and UMCL01-101 cells, and PKCβ1 alone in BCBL-1 cells. The viability of 2F7 and BCBL-1 cells decreased significantly in the presence of PKCβ-selective inhibitor at half-maximal inhibitory concentration of 14 and 15 μmol/L, respectively, as measured by tetrazolium dye reduction assay. In contrast, UMCL01-101 cells were relatively resistant. As determined using flow cytometric deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick-end labeling assay with propidium iodide staining, the responsiveness of sensitive cells was associated with apoptotic induction and cell cycle inhibition. Protein kinase C-beta-selective inhibition was observed not to affect AKT phosphorylation but to induce a rapid and sustained reduction in the phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta, ribosomal protein S6, and mammalian target of rapamycin in sensitive cell lines.
Conclusions: The results indicate that PKCβ plays an important role in AIDS-related NHL survival and suggest that PKCβ targeting should be considered in a broader spectrum of NHL. The observations in BCBL-1 were unexpected in the absence of PKCβ2 expression and implicate PKCβ1 as a regulator in those cells.
Figures





References
-
- Faivre S, Djelloul S, Raymond E. New paradigms in anticancer therapy: targeting multiple signaling pathways with kinase inhibitors. Semin Oncol. 2006;33:407–420. - PubMed
-
- Leonard JP, Martin P, Barrientos J, et al. Targeted treatment and new agents in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Semin Hematol. 2008;45:S11–16. - PubMed
-
- Serova M, Ghoul A, Benhadji KA, et al. Preclinical and clinical development of novel agents that target the protein kinase C family. Semin Oncol. 2006;33:466–478. - PubMed
-
- Wood C, Harrington W., Jr AIDS and associated malignancies. Cell Res. 2005;15:947–952. - PubMed
-
- Aoki Y, Tosato G. Neoplastic conditions in the context of HIV-1 infection. Curr HIV Res. 2004;2:343–349. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

