Impact of SORL1 single nucleotide polymorphisms on Alzheimer's disease cerebrospinal fluid markers
- PMID: 21997402
- PMCID: PMC3696367
- DOI: 10.1159/000332017
Impact of SORL1 single nucleotide polymorphisms on Alzheimer's disease cerebrospinal fluid markers
Abstract
Background: Recently, genetic variants of the neuronal sortilin-related receptor with A-type repeats (SORL1, also called LR11 or sorLA) have emerged as risk factors for the development of Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Methods: In this study, SORL1 gene polymorphisms, which have been shown to be related to AD, were analyzed for associations with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) amyloid beta1-42 (Aβ(1-42)), phosphorylated tau181, and total tau levels in a non-Hispanic Caucasian sample, which encompassed 100 cognitively healthy elderly individuals, 166 patients with mild cognitive impairment, and 87 patients with probable AD. The data were obtained from the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) database (www.loni.ucla.edu/ADNI). Moreover, the impact of gene-gene interactions between SORL1 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and the apolipoprotein E (APOE) ε4 allele, the major genetic risk factor for sporadic AD, on Aβ(1-42) concentrations was investigated.
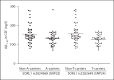
Results: Significant associations between CSF Aβ(1-42) levels and the SORL1 SNPs 23 (rs3824968) and 24 (rs2282649) were detected in the AD group. The latter association became marginally statistically insignificant after Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons. Carriers of the SORL1 SNP24 T allele and the SNP23 A allele both had lower CSF Aβ(1-42) concentrations than non-carriers of these alleles. The analysis of the impact of interactions between APOE ε4 allele and SORL1 SNPs on CSF Aβ(1-42) levels unraveled significant influences of APOE.
Conclusions: Our findings provide further support for the notion that SORL1 genetic variants are related to AD pathology, probably by regulating the amyloid cascade.
Copyright © 2011 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
References
-
- Rogaeva E, Meng Y, Lee JH, Gu Y, Kawarai T, Zou F, Katayama T, Baldwin CT, Cheng R, Hasegawa H, Chen F, Shibata N, Lunetta KL, Pardossi-Piquard R, Bohm C, Wakutani Y, Cupples LA, Cuenco KT, Green RC, Pinessi L, Rainero I, Sorbi S, Bruni A, Duara R, Friedland RP, Inzelberg R, Hampe W, Bujo H, Song YQ, Andersen OM, Willnow TE, Graff-Radford N, Petersen RC, Dickson D, Der SD, Fraser PE, Schmitt-Ulms G, Younkin S, Mayeux R, Farrer LA, St George-Hyslop P. The neuronal sortilin-related receptor SORL1 is genetically associated with Alzheimer disease. Nat Genet. 2007;39:168–177. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Feulner TM, Laws SM, Friedrich P, Wagenpfeil S, Wurst SH, Riehle C, Kuhn KA, Krawczak M, Schreiber S, Nikolaus S, Forstl H, Kurz A, Riemenschneider M. Examination of the current top candidate genes for AD in a genome-wide association study. Mol Psychiatry. 2010;15:756–766. - PubMed
-
- Bettens K, Brouwers N, Engelborghs S, De Deyn PP, Van Broeckhoven C, Sleegers K. SORL1 is genetically associated with increased risk for late-onset Alzheimer disease in the Belgian population. Hum Mutat. 2008;29:769–770. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous