Linking oxidative events to inflammatory and adaptive gene expression induced by exposure to an organic particulate matter component
- PMID: 21997482
- PMCID: PMC3279454
- DOI: 10.1289/ehp.1104055
Linking oxidative events to inflammatory and adaptive gene expression induced by exposure to an organic particulate matter component
Abstract
Background: Toxicological studies have correlated inflammatory effects of diesel exhaust particles (DEP) with its organic constituents, such as the organic electrophile 1,2-naphthoquinone (1,2-NQ).
Objective: To elucidate the mechanisms involved in 1,2-NQ-induced inflammatory responses, we examined the role of oxidant stress in 1,2-NQ-induced expression of inflammatory and adaptive genes in a human airway epithelial cell line.
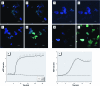
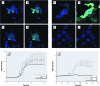
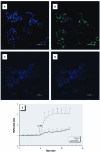
Methods: We measured cytosolic redox status and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in living cells using the genetically encoded green fluorescent protein (GFP)-based fluorescent indicators roGFP2 and HyPer, respectively. Expression of interleukin-8 (IL-8), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) mRNA was measured in BEAS-2B cells exposed to 1,2-NQ for 1-4 hr. Catalase overexpression and metabolic inhibitors were used to determine the role of redox changes and H2O2 in 1,2-NQ-induced gene expression.
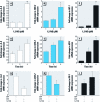
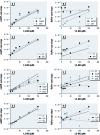
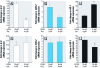
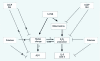
Results: Cells expressing roGFP2 and HyPer showed a rapid loss of redox potential and an increase in H2O2 of mitochondrial origin following exposure to 1,2-NQ. Overexpression of catalase diminished the H2O2-dependent signal but not the 1,2-NQ-induced loss of reducing potential. Catalase overexpression and inhibitors of mitochondrial respiration diminished elevations in IL-8 and COX-2 induced by exposure to 1,2-NQ, but potentiated HO-1 mRNA levels in BEAS cells.
Conclusion: These data show that 1,2-NQ exposure induces mitochondrial production of H2O2 that mediates the expression of inflammatory genes, but not the concurrent loss of reducing redox potential in BEAS cells. 1,2-NQ exposure also causes marked expression of HO-1 that appears to be enhanced by suppression of H2O2. These findings shed light into the oxidant-dependent events that underlie cellular responses to environmental electrophiles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no actual or potential competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bai Y, Suzuki AK, Sagai M. The cytotoxic effects of diesel exhaust particles on human pulmonary artery endothelial cells in vitro: role of active oxygen species. Free Radic Biol Med. 2001;30(5):555–562. - PubMed
-
- Becker S, Mundandhara S, Devlin RB, Madden M. Regulation of cytokine production in human alveolar macrophages and airway epithelial cells in response to ambient air pollution particles: further mechanistic studies. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2005;207(2) suppl:269–275. - PubMed
-
- Cho AK, Stefano ED, You Y, Rodriguez CE, Schmitz DA, Kumagai Y, et al. Determination of four quinones in diesel exhaust particles, SRM 1649a, and atmospheric PM2.5. Aerosol Sci Technol. 2004;38(S1):68–81.
-
- Endo A, Sumi D, Kumagai Y. 1,2-Naphthoquinone disrupts the function of cAMP response element-binding protein through covalent modification. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;361(1):243–248. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
