Principles and applications of diffusion-weighted imaging in cancer detection, staging, and treatment follow-up
- PMID: 21997994
- PMCID: PMC8996338
- DOI: 10.1148/rg.316115515
Principles and applications of diffusion-weighted imaging in cancer detection, staging, and treatment follow-up
Abstract
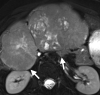
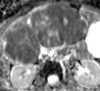
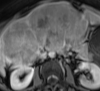
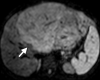
Diffusion-weighted imaging relies on the detection of the random microscopic motion of free water molecules known as Brownian movement. With the development of new magnetic resonance (MR) imaging technologies and stronger diffusion gradients, recent applications of diffusion-weighted imaging in whole-body imaging have attracted considerable attention, especially in the field of oncology. Diffusion-weighted imaging is being established as a pivotal aspect of MR imaging in the evaluation of specific organs, including the breast, liver, kidney, and those in the pelvis. When used in conjunction with apparent diffusion coefficient mapping, diffusion-weighted imaging provides information about the functional environment of water in tissues, thereby augmenting the morphologic information provided by conventional MR imaging. Detected changes include shifts of water from extracellular to intracellular spaces, restriction of cellular membrane permeability, increased cellular density, and disruption of cellular membrane depolarization. These findings are commonly associated with malignancies; therefore, diffusion-weighted imaging has many applications in oncologic imaging and can aid in tumor detection and characterization and in the prediction and assessment of response to therapy.
© RSNA, 2011.
Figures



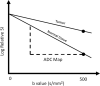
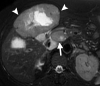
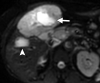
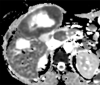


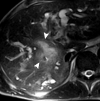

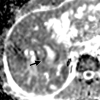
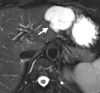

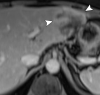








References
-
- Koh DM, Collins DJ. Diffusion-weighted MRI in the body: applications and challenges in oncology. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2007;188(6):1622–1635. - PubMed
-
- Taouli B, Koh DM. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the liver. Radiology 2010;254(1):47–66. - PubMed
-
- desouza NM, Reinsberg SA, Scurr ED, Brewster JM, Payne GS. . Magnetic resonance imaging in prostate cancer: the value of apparent diffusion coefficients for identifying malignant nodules. Br J Radiol 2007;80(950):90–95. - PubMed
-
- Sinha S, Lucas-Quesada FA, Sinha U, DeBruhl N, Bassett LW. In vivo diffusion-weighted MRI of the breast: potential for lesion characterization. J Magn Reson Imaging 2002;15(6):693–704. - PubMed
-
- Kwee TC, Takahara T, Ochiai R, et al. . Whole-body diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Eur J Radiol 2009;70(3):409–417. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

