Crucial role of CD40 signaling in vascular wall cells in neointimal formation and vascular remodeling after vascular interventions
- PMID: 21998133
- PMCID: PMC3241889
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.238329
Crucial role of CD40 signaling in vascular wall cells in neointimal formation and vascular remodeling after vascular interventions
Abstract
Objective: It has been shown that CD40-TRAF6 axis in leukocytes plays a significant role in neointimal formation after carotid ligation. Because CD40 and TRAF6 are expressed not only in leukocytes but also in vascular cells, we examined the role of CD40 contributed by vascular wall cells in neointimal formation after carotid ligation in an atherogenic environment.
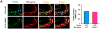
Methods and results: Both CD40 and TRAF6 in medial smooth muscle cells (SMCs) was upregulated significantly at 3 days and more prominently at 7 days after injury in wildtype mice, but the TRAF6 upregulation was abolished in CD40(-/-) mice. In vitro, TRAF6 expression was induced by cytokines (tumor necrosis factor -α, interleukin-1β) via a NF-κB-dependent manner in wildtype SMCs, but this induction was blocked in CD40-deficient SMCs. Bone marrow chimeras revealed a comparable reduction in neointimal formation and lumen stenosis in mice lacking either vascular wall- or bone marrow-associated CD40. Lacking vascular wall-associated CD40 resulted in a significant reduction in monocyte/macrophage accumulation, NF-κB activation, and multiple proinflammatory mediators (ICAM-1, VCAM-1, MCP-1, MMP-9, tissue factor). In vitro data confirmed that CD40 deficiency or TRAF6 knockdown suppressed CD40L-induced proinflammatory phenotype of SMCs by inhibition of NF-κB activation. Moreover, both in vivo and in vitro data showed that CD40 deficiency prevented injury-induced SMC apoptosis but did not affect SMC proliferation and migration.
Conclusions: CD40 signaling through TRAF6 in vascular SMCs seems to be centrally involved in neointimal formation in a NF-κB-dependent manner. Modulating CD40 signaling on local vascular wall may become a new therapeutic target against vascular restenosis.
Figures




























References
-
- Zargham R. Preventing restenosis after angioplasty: a multistage approach. Clin Sci (Lond) 2008;114:257–264. - PubMed
-
- Donners MM, Daemen MJ, Cleutjens KB, Heeneman S. Inflammation and restenosis: implications for therapy. Ann Med. 2003;35:523–531. - PubMed
-
- Lievens D, Eijgelaar WJ, Biessen EA, Daemen MJ, Lutgens E. The multi-functionality of CD40L and its receptor CD40 in atherosclerosis. Thromb Haemost. 2009;102:206–214. - PubMed
-
- Santilli F, Basili S, Ferroni P, Davì G. CD40/CD40L system and vascular disease. Intern Emerg Med. 2007;2:256–268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

