Clinical significance of SF3B1 mutations in myelodysplastic syndromes and myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasms
- PMID: 21998214
- PMCID: PMC3236114
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-09-377275
Clinical significance of SF3B1 mutations in myelodysplastic syndromes and myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasms
Abstract
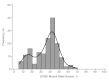
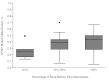
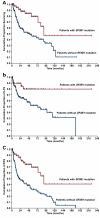
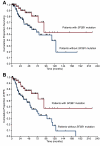
In a previous study, we identified somatic mutations of SF3B1, a gene encoding a core component of RNA splicing machinery, in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). Here, we define the clinical significance of these mutations in MDS and myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasms (MDS/MPN). The coding exons of SF3B1 were screened using massively parallel pyrosequencing in patients with MDS, MDS/MPN, or acute myeloid leukemia (AML) evolving from MDS. Somatic mutations of SF3B1 were found in 150 of 533 (28.1%) patients with MDS, 16 of 83 (19.3%) with MDS/MPN, and 2 of 38 (5.3%) with AML. There was a significant association of SF3B1 mutations with the presence of ring sideroblasts (P < .001) and of mutant allele burden with their proportion (P = .002). The mutant gene had a positive predictive value for ring sideroblasts of 97.7% (95% confidence interval, 93.5%-99.5%). In multivariate analysis including established risk factors, SF3B1 mutations were found to be independently associated with better overall survival (hazard ratio = 0.15, P = .025) and lower risk of evolution into AML (hazard ratio = 0.33, P = .049). The close association between SF3B1 mutations and disease phenotype with ring sideroblasts across MDS and MDS/MPN is consistent with a causal relationship. Furthermore, SF3B1 mutations are independent predictors of favorable clinical outcome, and their incorporation into stratification systems might improve risk assessment in MDS.
Figures
Comment in
-
It dices, it splices!Blood. 2011 Dec 8;118(24):6237-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-10-386540. Blood. 2011. PMID: 22161850 No abstract available.
References
-
- Cazzola M, Malcovati L. Myelodysplastic syndromes: coping with ineffective hematopoiesis. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(6):536–538. - PubMed
-
- Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, et al. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Lyon, France: IARC; 2008.
-
- Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber DA, et al. The 2008 revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: rationale and important changes. Blood. 2009;114(5):937–951. - PubMed
-
- Greenberg P, Cox C, LeBeau MM, et al. International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 1997;89(6):2079–2088. - PubMed
-
- Malcovati L, Della Porta M, Pascutto C, et al. Prognostic factors and life expectancy in myelodysplastic syndromes classified according to WHO criteria: a basis for clinical decision-making. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:7594–7603. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

