From stem cell to red cell: regulation of erythropoiesis at multiple levels by multiple proteins, RNAs, and chromatin modifications
- PMID: 21998215
- PMCID: PMC3236116
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-07-356006
From stem cell to red cell: regulation of erythropoiesis at multiple levels by multiple proteins, RNAs, and chromatin modifications
Abstract
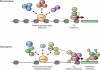
This article reviews the regulation of production of RBCs at several levels. We focus on the regulated expansion of burst-forming unit-erythroid erythroid progenitors by glucocorticoids and other factors that occur during chronic anemia, inflammation, and other conditions of stress. We also highlight the rapid production of RBCs by the coordinated regulation of terminal proliferation and differentiation of committed erythroid colony-forming unit-erythroid progenitors by external signals, such as erythropoietin and adhesion to a fibronectin matrix. We discuss the complex intracellular networks of coordinated gene regulation by transcription factors, chromatin modifiers, and miRNAs that regulate the different stages of erythropoiesis.
Figures

References
-
- Palis J, Robertson S, Kennedy M, Wall C, Keller G. Development of erythroid and myeloid progenitors in the yolk sac and embryo proper of the mouse. Development. 1999;126(22):5073–5084. - PubMed
-
- Elliott S, Pham E, Macdougall IC. Erythropoietins: a common mechanism of action. Exp Hematol. 2008;36(12):1573–1584. - PubMed
-
- Fawcett DW. Bloom & Fawcett: Concise Histology. 1st ed. Oxford, United Kingdom: Arnold Publishers; 1997.
-
- Molineux G, Foote M, Elliott S. Erythropoiesis and Erythropoietins. 2nd ed. Basel, Switzerland: Birkhauser; 2009.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

