The orchestration of mammalian tissue morphogenesis through a series of coherent feed-forward loops
- PMID: 21998302
- PMCID: PMC3234836
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.264580
The orchestration of mammalian tissue morphogenesis through a series of coherent feed-forward loops
Abstract
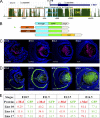
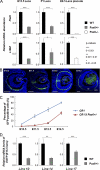
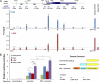
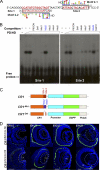
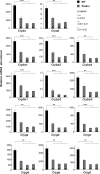
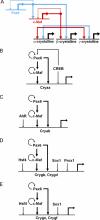
Tissue morphogenesis requires intricate temporal and spatial control of gene expression that is executed through specific gene regulatory networks (GRNs). GRNs are comprised from individual subcircuits of different levels of complexity. An important question is to elucidate the mutual relationship between those genes encoding DNA-binding factors that trigger the subcircuit with those that play major "later" roles during terminal differentiation via expression of specific genes that constitute the phenotype of individual tissues. The ocular lens is a classical model system to study tissue morphogenesis. Pax6 is essential for both lens placode formation and subsequent stages of lens morphogenesis, whereas c-Maf controls terminal differentiation of lens fibers, including regulation of crystallins, key lens structural proteins required for its transparency and refraction. Here, we show that Pax6 directly regulates c-Maf expression during lens development. A 1.3-kb c-Maf promoter with a 1.6-kb upstream enhancer (CR1) recapitulated the endogenous c-Maf expression pattern in lens and retinal pigmented epithelium. ChIP assays revealed binding of Pax6 and c-Maf to multiple regions of the c-Maf locus in lens chromatin. To predict functional Pax6-binding sites, nine novel variants of Pax6 DNA-binding motifs were identified and characterized. Two of these motifs predicted a pair of Pax6-binding sites in the CR1. Mutagenesis of these Pax6-binding sites inactivated transgenic expression in the lens but not in retinal pigmented epithelium. These data establish a novel regulatory role for Pax6 during lens development, link together the Pax6/c-Maf/crystallin regulatory network, and suggest a novel type of GRN subcircuit that controls a major part of embryonic lens development.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

