Deficiency for costimulatory receptor 4-1BB protects against obesity-induced inflammation and metabolic disorders
- PMID: 21998397
- PMCID: PMC3219944
- DOI: 10.2337/db10-1805
Deficiency for costimulatory receptor 4-1BB protects against obesity-induced inflammation and metabolic disorders
Abstract
Objective: Inflammation is an important factor in the development of insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and fatty liver disease. As a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily (TNFRSF9) expressed on immune cells, 4-1BB/CD137 provides a bidirectional inflammatory signal through binding to its ligand 4-1BBL. Both 4-1BB and 4-1BBL have been shown to play an important role in the pathogenesis of various inflammatory diseases.
Research design and methods: Eight-week-old male 4-1BB-deficient and wild-type (WT) mice were fed a high-fat diet (HFD) or a regular diet for 9 weeks.
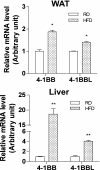
Results: We demonstrate that 4-1BB deficiency protects against HFD-induced obesity, glucose intolerance, and fatty liver disease. The 4-1BB-deficient mice fed an HFD showed less body weight gain, adiposity, adipose infiltration of macrophages/T cells, and tissue levels of inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, interleukin-6, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 [MCP-1]) compared with HFD-fed control mice. HFD-induced glucose intolerance/insulin resistance and fatty liver were also markedly attenuated in the 4-1BB-deficient mice.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that 4-1BB and 4-1BBL may be useful therapeutic targets for combating obesity-induced inflammation and metabolic disorders.
Figures




Comment in
-
Comment on: Kim et al. Deficiency for costimulatory receptor 4-1BB protects against obesity-induced inflammation and metabolic disorders. Diabetes 2011;60:3159-3168.Diabetes. 2012 Jul;61(7):e6; author reply e7. doi: 10.2337/db12-0128. Diabetes. 2012. PMID: 22723280 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

