Effect of rosiglitazone on bone quality in a rat model of insulin resistance and osteoporosis
- PMID: 21998400
- PMCID: PMC3219933
- DOI: 10.2337/db10-1672
Effect of rosiglitazone on bone quality in a rat model of insulin resistance and osteoporosis
Abstract
Objective: Rosiglitazone (RSG) is an insulin-sensitizing drug used to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus. The A Diabetes Outcome Progression Trial (ADOPT) shows that women taking RSG experienced more fractures than patients taking other type 2 diabetes drugs. These were not osteoporotic vertebral fractures but, rather, occurred in the limbs. The purpose of this study was to investigate how RSG treatment alters bone quality, which leads to fracture risk, using the Zucker fatty rat as a model.
Research design and methods: A total of 61 female 4-month-old rats were divided into six groups. One Sham group was a control and another was administered oral RSG 10 mg/kg/day. Four ovariectomized (OVX) groups were dosed as follows: controls, RSG 10 mg/kg, alendronate (ALN, injected at 0.7 mg/kg/week), and RSG 10 mg/kg plus ALN. After 12 weeks of treatment, bone quality was evaluated by mechanical testing. Microarchitecture, bone mineral density (BMD), cortical bone porosity, and bone remodeling were also measured.
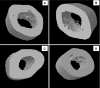
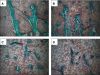
Results: OVX RSG 10 mg/kg rats had lower vertebral BMD and compromised trabecular architecture versus OVX controls. Increased cortical bone porosity and decreased mechanical properties occurred in these rats. ALN treatment prevented decreased BMD and architectural and mechanical properties in the OVX model. Reduced bone formation, increased marrow adiposity, and excess bone resorption were observed in RSG-treated rats.
Conclusions: RSG decreases bone quality. An unusual finding was an increase in cortical bone porosity induced by RSG, consistent with its effect on long bones of women. ALN, an inhibitor of bone resorption, enhanced mechanical strength and may provide an approach to partially counter the deleterious skeletal effects of RSG.
Figures
References
-
- Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Shaw J. Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature 2001;414:782–787 - PubMed
-
- Walker AB, Chattington PD, Buckingham RE, Williams G. The thiazolidinedione rosiglitazone (BRL-49653) lowers blood pressure and protects against impairment of endothelial function in Zucker fatty rats. Diabetes 1999;48:1448–1453 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

