Sudden death from systemic rotavirus infection and detection of nonstructural rotavirus proteins
- PMID: 21998424
- PMCID: PMC3232974
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01303-11
Sudden death from systemic rotavirus infection and detection of nonstructural rotavirus proteins
Abstract
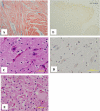
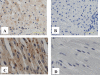
A 2.5-year-old girl died suddenly during the course of rotavirus gastroenteritis. The autopsy showed encephalopathy with rotavirus systemic infection. Here, we provide evidence of rotavirus replication in multiple organs. Our findings clarify that rotavirus infection in children can extend beyond the intestinal tract through viremia.
Figures
References
-
- Ciok A. M., Nuovo G. J. 2002. Histologic and in situ viral findings in the myocardium in cases of sudden, unexpected death. Mod. Pathol. 15: 914–922 - PubMed
-
- Finehout E. J., Franck Z., Relkin N., Lee K. H. 2006. Proteomic analysis of cerebrospinal fluid changes related to postmortem interval. Clin. Chem. 52: 1906–1913 - PubMed
-
- Gilger M. A., et al. 1992. Extraintestinal rotavirus infections in children with immunodeficiency. J. Pediatr. 120: 912–917 - PubMed
-
- Ioi H., et al. 2005. A case of Reye syndrome with rotavirus infection accompanied with high cytokines. J. Infect. 52: e124–128 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

