Computational modeling of allosteric communication reveals organizing principles of mutation-induced signaling in ABL and EGFR kinases
- PMID: 21998569
- PMCID: PMC3188506
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002179
Computational modeling of allosteric communication reveals organizing principles of mutation-induced signaling in ABL and EGFR kinases
Abstract
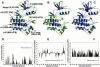
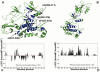
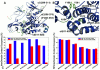
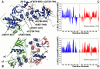
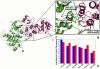
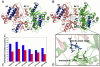
The emerging structural information about allosteric kinase complexes and the growing number of allosteric inhibitors call for a systematic strategy to delineate and classify mechanisms of allosteric regulation and long-range communication that control kinase activity. In this work, we have investigated mechanistic aspects of long-range communications in ABL and EGFR kinases based on the results of multiscale simulations of regulatory complexes and computational modeling of signal propagation in proteins. These approaches have been systematically employed to elucidate organizing molecular principles of allosteric signaling in the ABL and EGFR multi-domain regulatory complexes and analyze allosteric signatures of the gate-keeper cancer mutations. We have presented evidence that mechanisms of allosteric activation may have universally evolved in the ABL and EGFR regulatory complexes as a product of a functional cross-talk between the organizing αF-helix and conformationally adaptive αI-helix and αC-helix. These structural elements form a dynamic network of efficiently communicated clusters that may control the long-range interdomain coupling and allosteric activation. The results of this study have unveiled a unifying effect of the gate-keeper cancer mutations as catalysts of kinase activation, leading to the enhanced long-range communication among allosterically coupled segments and stabilization of the active kinase form. The results of this study can reconcile recent experimental studies of allosteric inhibition and long-range cooperativity between binding sites in protein kinases. The presented study offers a novel molecular insight into mechanistic aspects of allosteric kinase signaling and provides a quantitative picture of activation mechanisms in protein kinases at the atomic level.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Koshland DE, Némethy G, Filmer D. Comparison of experimental binding data and theoretical models in proteins containing subunits. Biochemistry. 1966;5:365–385. - PubMed
-
- Monod J, Wyman J, Changeux JP. On the nature of allosteric transitions: A plausible model. J Mol Biol. 1965;12:88–118. - PubMed
-
- Goodey NM, Benkovic SJ. Allosteric regulation and catalysis emerge via a common route. Nat Chem Biol. 2008;4:474–482. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

