Esculetin inhibits N-methyl-D-aspartate neurotoxicity via glutathione preservation in primary cortical cultures
- PMID: 21998617
- PMCID: PMC3188735
- DOI: 10.5625/lar.2011.27.3.259
Esculetin inhibits N-methyl-D-aspartate neurotoxicity via glutathione preservation in primary cortical cultures
Abstract
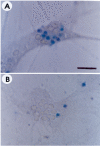
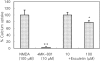
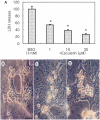
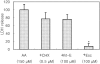
Recently, loss of endogenous glutathione during N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor-mediated excitotoxic injury, and the resultant overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) through an arachidonic acid cascade process in brain, have been implicated in neuronal damage in various neurodegenerative diseases. Glutathione depletion induced by L-buthionine-(S,R)-sulfoximine (BSO), an inhibitor of glutathione synthesis, is known to cause arachidonic acid-mediated excitotoxicity in primary mixed cortical cultures. The aim of this study was to investigate whether esculetin (6,7-dihydroxycoumarin), an inhibitor of lipoxygenase, protects against neurotoxicity induced by NMDA or BSO. We observed that neurotoxicity induced by NMDA but not kainic acid was attenuated by esculetin. At the same concentration (100 µM), esculetin attenuated the (45)Ca(2+) uptake elevation induced by NMDA. Free radical-mediated neuronal injury induced by H(2)O(2) and xanthine/xanthine oxidase was concentration-dependently blocked by esculetin. Esculetin (1-30 µM) dose-dependently inhibited BSO-induced neuronal injury. In addition, arachidonate-induced neurotoxicity was completely blocked by esculetin. BSO also reduced glutathione peroxidase (GPx) activity, but did not change glutathione reductase (GR) activity 24 h after treatment. Esculetin dose-dependently increased GR activity, but did not alter GPx activity. These findings suggest that esculetin can contribute to the rescue of neuronal cells from NMDA neurotoxicity and that this protective effect occurs partly through NMDA receptor modulation and the sparing of glutathione depletion.
Keywords: Esculetin; L-buthionine-(S,R)-sulfoximine; N-methyl-D-aspartate; cortical cultures; lipoxygenase.
Figures
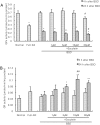
References
-
- Dumuis A, Sebben M, Haynes L, Pin JP, Bockaert J. NMDA receptors activate the arachidonic acid cascade system in striatal neurons. Nature. 1988;336(6194):68–70. - PubMed
-
- Almeida A, Heales SJ, Bolaños JP, Medina JM. Glutamate neurotoxicity is associated with nitric oxide-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction and glutathione depletion. Brain Res. 1998;790(1-2):209–216. - PubMed
-
- Taylor AL, Hewett SJ. Potassium-evoked glutamate release liberates arachidonic acid from cortical neurons. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(46):43881–43887. - PubMed
-
- Collingridge GL, Singer W. Excitatory amino acid receptors and synaptic plasticity. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990;11(7):290–296. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez-Alvarez J, Blanco I, Patel AJ. Modulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor mediated arachidonic acid release by endogenous nitric oxide in cultured neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1996;218(2):95–98. - PubMed

