MMP-10/stromelysin-2 promotes invasion of head and neck cancer
- PMID: 21998657
- PMCID: PMC3187776
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025438
MMP-10/stromelysin-2 promotes invasion of head and neck cancer
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2012;7(2). doi: 10.1371/annotation/ef18e199-e66d-43b9-97e0-96d1ab149193. Kiekhaee, Mohammad Reza [corrected to Keikhaee, Mohammad Reza] doi: 10.1371/annotation/ef18e199-e66d-43b9-97e0-96d1ab149193
Abstract
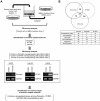
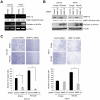
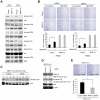
Background: Periostin, IFN-induced transmembrane protein 1 (IFITM1) and Wingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 5B (Wnt-5b) were previously identified as the invasion promoted genes of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) by comparing the gene expression profiles between parent and a highly invasive clone. We have previously reported that Periostin and IFITM1 promoted the invasion of HNSCC cells. Here we demonstrated that Wnt-5b overexpression promoted the invasion of HNSCC cells. Moreover, stromelysin-2 (matrix metalloproteinase-10; MMP-10) was identified as a common up-regulated gene among Periostin, IFITM1 and Wnt-5b overexpressing HNSCC cells by using microarray data sets. In this study, we investigated the roles of MMP-10 in the invasion of HNSCC.
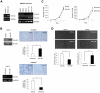
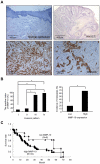
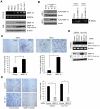
Methods and findings: We examined the expression of MMP-10 in HNSCC cases by immunohistochemistry. High expression of MMP-10 was frequently observed and was significantly correlated with the invasiveness and metastasis in HNSCC cases. Next, we examined the roles of MMP-10 in the invasion of HNSCC cells in vitro. Ectopic overexpression of MMP-10 promoted the invasion of HNSCC cells, and knockdown of MMP-10 suppressed the invasion of HNSCC cells. Moreover, MMP-10 knockdown suppressed Periostin and Wnt-5b-promoted invasion. Interestingly, MMP-10 overexpression induced the decreased p38 activity and MMP-10 knockdown induced the increased p38 activity. In addition, treatment with a p38 inhibitor SB203580 in HNSCC cells inhibited the invasion.
Conclusions: These results suggest that MMP-10 plays an important role in the invasion and metastasis of HNSCC, and that invasion driven by MMP-10 is partially associated with p38 MAPK inhibition. We suggest that MMP-10 can be used as a marker for prediction of metastasis in HNSCC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Mao L, Hong WK, Papadimitrakopoulou VA. Focus on head and neck cancer. Cancer Cell. 2004;5:311–316. - PubMed
-
- Neville BW, Damm DD, Allen CM, Bouquot JE. Epithelial Pthology. Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. Edited by Neville BW. Philadelphia, W B Saunders. 1995;295-302
-
- Mamelle G, Pampurik J, Luboinski B, Lancer R, Lusinchi A, et al. Lymph node prognostic factors in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Am J Surg. 1994;168:494–498. - PubMed
-
- Fidler IJ. Critical factors in the biology of human cancer metastasis: Twenty-eighth GHA Clowes Memorial Award Lecture. Cancer Res. 1990;50:6130–6138. - PubMed
-
- Howell GMS, Grandis JR. Molecular mediators of metastasis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck. 2005;27:710–717. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

