The B-Raf status of tumor cells may be a significant determinant of both antitumor and anti-angiogenic effects of pazopanib in xenograft tumor models
- PMID: 21998674
- PMCID: PMC3187787
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025625
The B-Raf status of tumor cells may be a significant determinant of both antitumor and anti-angiogenic effects of pazopanib in xenograft tumor models
Abstract
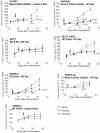
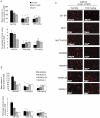
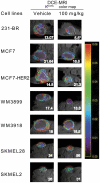
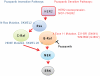
Pazopanib is an FDA approved Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor inhibitor. We previously reported that it also inhibits tumor cell B-Raf activity in an experimental brain metastatic setting. Here, we determine the effects of different B-Raf genotypes on pazopanib efficacy, in terms of primary tumor growth and anti-angiogenesis. A panel of seven human breast cancer and melanoma cell lines harboring different mutations in the Ras-Raf pathway was implanted orthotopically in mice, and tumor growth, ERK1/2, MEK1/2 and AKT activation, and blood vessel density and permeability were analyzed. Pazopanib was significantly inhibitory to xenografts expressing either exon 11 mutations of B-Raf, or HER2 activated wild type B-Raf; no significant inhibition of a xenograft expressing the common V600E B-Raf mutation was observed. Decreased pMEK staining in the responsive tumors confirmed that B-Raf was targeted by pazopanib. Interestingly, pazopanib inhibition of tumor cell B-Raf also correlated with its anti-angiogenic activity, as quantified by vessel density and area. In conclusion, using pazopanib, tumor B-Raf status was identified as a significant determinant of both tumor growth and angiogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Kumar R, Knick VB, Rudolph SK, Johnson JH, Crosby RM, et al. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic correlation from mouse to human with pazopanib, a multikinase angiogenesis inhibitor with potent antitumor and antiangiogenic activity. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6:2012–2021. - PubMed
-
- Kusters B, Leenders WP, Wesseling P, Smits D, Verrijp K, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor-A(165) induces progression of melanoma brain metastases without induction of sprouting angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2002;62:341–345. - PubMed
-
- Leenders W, Kusters B, Verrijp K, Maass C, Wesseling P, et al. Antiangiogenic Therapy of Cerebral Melanoma Metastases Results in Sustained Tumor Progression via Vessel Co-Option. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:6222–6230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

