MiR-29a inhibits cell proliferation and induces cell cycle arrest through the downregulation of p42.3 in human gastric cancer
- PMID: 21998710
- PMCID: PMC3187799
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025872
MiR-29a inhibits cell proliferation and induces cell cycle arrest through the downregulation of p42.3 in human gastric cancer
Abstract
As a newly identified and characterized gene, p42.3 is associated with cell proliferation and tumorigenicity. The expression of p42.3 is upregulated in human gastric cancer (GC), but its underlying mechanisms of action are not well understood. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are known to play vital regulatory roles in many cellular processes. Here we utilized bioinformatics and experimental approaches to investigate the regulatory relationship between miRNAs and the p42.3 gene. We showed that miR-29a could repress p42.3 expression at both the mRNA and protein levels via directly binding to its 3'UTR. Furthermore, an inverse relationship was observed between miR-29a and p42.3 expression in gastric cancer cell lines and GC tissue samples, especially in cases where p42.3 was downregulated. Taken together, we have elucidated previously unrecognized roles of miR-29a and indicated that miR-29a may function, at least partially, by targeting the p42.3 gene in human GC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

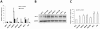
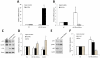

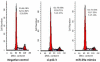

References
-
- Xu X, Li W, Fan X, Liang Y, Zhao M, et al. Identification and characterization of a novel p42.3 gene as tumor-specific and mitosis phase-dependent expression in gastric cancer. Oncogene. 2007;52:7371–7379. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;2:281–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

